Immuno-oncology is a way to treat cancer by using the body’s immune system. BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) technology is a targeted immuno-oncology platform that binds a patient’s own T cells to cancer cells. Because BiTE technology is flexible, it is easy to make molecules that attack tumor-specific antigens, which makes immuno-oncotherapy possible. Blinatumomab was the first standard BiTE molecule to be approved. It targets CD19 surface antigens on B cells and is mostly unaffected by genetic changes or escape mechanisms inside cells. More BiTE molecules are being made to treat other blood cancers (like multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukaemia, and B-cell არაჰოჯკინის ლიმფომა) and solid tumours (like prostate cancer, glioblastoma, stomach cancer, and small-cell lung cancer). BiTE molecules that have a longer half-life than the standard ones are also being made. With BiTE technology, advances in immuno-oncology could make it easier to treat both blood and solid tumours and make them more effective when used with other treatments.
რა არის BiTe თერაპია?
Immuno-oncology therapies are scientifically proven ways to treat different types of solid and სისხლის კიბოები. Hematologic cancers are a good fit for treatments that target the immune system because cancerous blood cells move around with immune cells. Several იმუნოთერაპია კიბოს მკურნალობა მიმდინარეობს.
Monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitors that stop the binding of checkpoint proteins (like PD-1 and CTLA-4) are useful against many types of cancer. They work well and are safe for many solid tumours, especially when they target PD-1. Non-small-cell lung, kidney, and bladder cancers have all been treated successfully with these drugs. But many people don’t react to checkpoint inhibitors or get sick again after taking them. Except for non-Hodgkin ლიმფომა, most results on hematologic cancers have been disappointing, especially for myeloma and leukaemia, where the overall response rate in approved indications ranges from 12.0% to 48.5%.8-15.
Other immuno-oncology treatments, on the other hand, have a higher success rate. Chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies change a patient’s T cells to attack a specific cellular antigen, such as CD19 in the treatment of B-cell malignancies and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in the treatment of მრავალჯერადი მიელომა (MM). CAR T-cell treatments have shown promise in treating hematologic cancers. They haven’t been as effective in treating solid tumours, but there have been some good results with ნეირობლასტომი, human epidermal growth factor receptor tumours, and non-small-cell lung cancer. The genetic modification and in vitro multiplication of T cells take a long and complicated manufacturing process. This is a downside of this therapy because it makes it harder for patients to get this treatment quickly and in large numbers. The fact that lymphodepletion through chemotherapy preparation must be done first as a requirement for improved effectiveness is also a drawback.
BiTE (ბისპეციფიკური T- უჯრედების შემქმნელი) თერაპია აკავშირებს პაციენტის საკუთარ T უჯრედებს სიმსივნის გამოხატულ ანტიგენებთან. ეს ააქტიურებს პაციენტის საკუთარი T უჯრედების ციტოტოქსიურ უნარს, მოკლას კიბო T უჯრედების გენების შეცვლისა და სხეულის გარეთ მათი ზრდის ან მანიპულირების გარეშე. BiTE მოლეკულები შეიძლება გამოყენებულ იქნას მარტო წამლად ან სხვა სამკურნალო საშუალებებთან ერთად, რათა უფრო ეფექტური გახდეს.
BiTe მოქმედების მექანიზმი
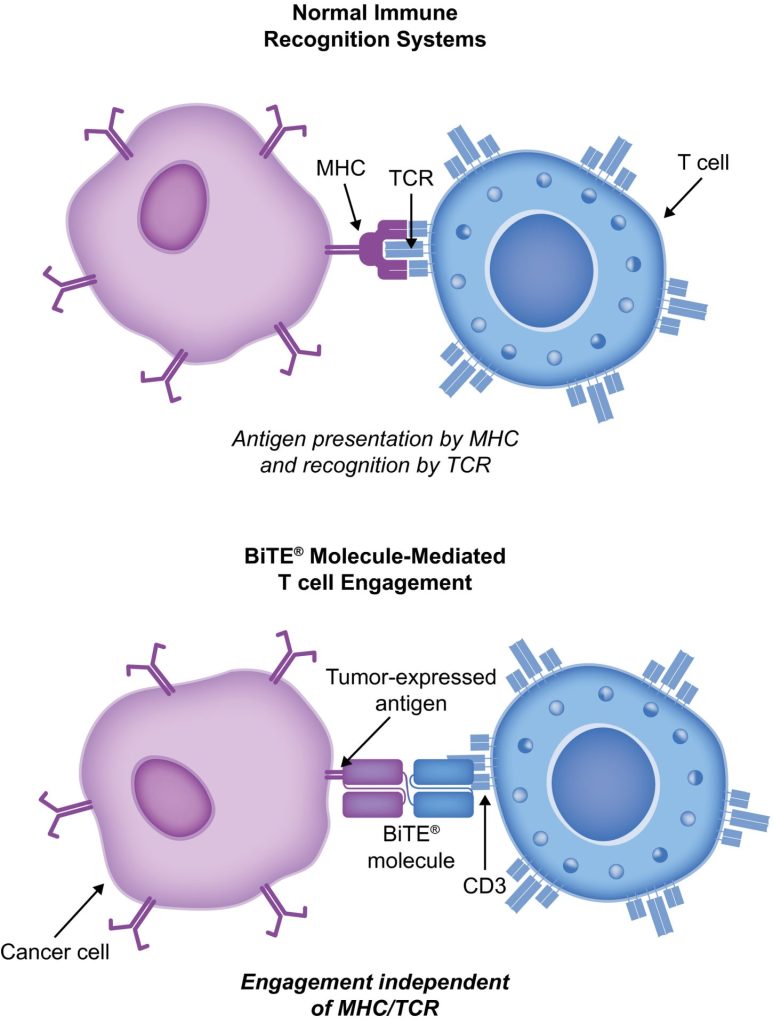
BiTE molecules are antibody constructs with two binding domains. One recognises tumor-expressed antigens (such as BCMA, CD19, or -like protein [DLL3]), and the other, CD3, recognises T cells (Fig. 1). Two single-chain variable fragment (scFv) regions from monoclonal antibodies are connected by a flexible peptide linker to make the binding domains. The first scFv binding region can be changed to target any surface antigen, so it can be used right away to treat a wide range of tumours and can be used again later. The second scFv binding region always binds to CD3, which is a part of the T-cell receptor complex that never changes. When a BiTE molecule interacts with both a cytotoxic T cell and a tumour cell, the T cells begin to multiply. This increases the amount of effector cells and makes BiTE therapy more effective. Then, the death of cancer cells is started. BiTE molecules can get any T cells to do this because they don’t need co-stimulation or the usual processes of the major histocompatibility complex.
Blinatumomab is the first and only BiTE therapy that has been approved. It targets the CD19 receptor on both normal and cancerous B cells. It is a highly potent molecule with cytotoxic effects seen at low exposures (10–100 pg/mL)26. In its presence, T cells can perform serial-target lysis, quickly binding to and killing many cells. This is how BiTE therapies work, and it can be seen in other BiTE molecules that are still in research. In მწვავე ლიმფობლასტური ლეიკემია (ALL), blinatumomab has been shown to be effective and safe. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration gave it fast approval, and in 2017, it got full approval for relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL. In 2018, accelerated approval was given to ბლინატუმომაბი for treating BCP-ALL with minimum residual disease (MRD). This was the first approval for this use. In November 2015, the European Medicines Agency also gave it a green light for BCP-ALL with a Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) that is negative and R/R. Blinatumomab is approved for R/R BCP-ALL in adults and children in 57 countries, including Japan, all countries in the European Union, Canada, and Australia.
ბლინატუმომაბი BCP-ALL-ით დაავადებულთა სამკურნალოდ
ბლინატუმომაბმა შეცვალა BCP-ALL მკურნალობის მეთოდი. სტანდარტული მოვლის (SOC) ქიმიოთერაპიასთან შედარებით, მან გაზარდა საერთო გადარჩენა (OS) და შეამცირა გარკვეული გვერდითი მოვლენების რაოდენობა (AEs). რამდენიმე მნიშვნელოვანი კვლევა, მათ შორის რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებადი კვლევები, აჩვენა, რომ ბლინატუმომაბი უსაფრთხოა და მუშაობს BCP-ALL-ზე როგორც მოზრდილებში, ასევე ბავშვებში. CAR T- უჯრედების თერაპიაარსებობს მხოლოდ მონაცემები 2 ერთჯერადი კვლევისგან (clinicaltrials.gov IDs NCT01626495 და NCT01029366), რომლებშიც მკურნალობდნენ 25 ბავშვი (5-22 წლის) და 5 ზრდასრული (26-60 წლამდე) R/R BCP-ALL და T-cell ALL. მაგრამ შედეგები იმედისმომცემია (სრული პასუხი [CR] 90%–ში, მდგრადი რემისია 6–თვიანი მოვლენის გარეშე გადარჩენით 67%–ში და საერთო გადარჩენის [OS] მაჩვენებელი 78% [საშუალო დაკვირვება, 7 თვე; დიაპაზონი, 1–24 თვე]).
TOWER კვლევა (ფაზა 3, რანდომიზებული, ღია ეტიკეტირების კვლევა, რომელიც იკვლევს BiTE ანტისხეულის ბლინატუმომაბის ეფექტურობას პრემდენი ქიმიოთერაპიის წინააღმდეგ მოვლის სტანდარტულ სუბიექტებში მორეციდივე/რეფრაქტორული B-წინამორბედი ALL; კლინიკურიტრიals.gov იდენტიფიკატორი NCT02013167 მოზრდილებში შედარებული მონოთერაპიის ეფექტურობაზე). s Ph-უარყოფით, R/R BCP-ALL. იმის გამო, რომ ადამიანები უფრო მეტხანს ცხოვრობდნენ, კვლევა ადრე შეწყდა. AE-ები ბლინატუმომაბის ჯგუფში იგივე იყო, რაც ადრე კვლევებში იყო ნანახი და ბლინატუმომაბს ჰქონდა უფრო დაბალი ექსპოზიციაზე მორგებული AE სიხშირე, ვიდრე SOC.34 ბლინატუმომაბი ასევე მუშაობს Ph-დადებითი, R/R BCP-ALL და Ph-უარყოფითი, R/R BCP-ALL მქონე ადამიანებისთვის.
30% to 50% of people with BCP-ALL in complete hematologic remission show persistent MRD. In the single-arm, phase 2 BLAST study (A Confirmatory Multicenter, Single-Arm Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of the BiTE Antibody Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With MRD of B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia; clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01207388), blinatumomab was tested on patients with BCP-ALL in first or later complete After blinatumomab treatment, 78% of patients who were MRD positive became MRD negative. The 5-year OS study showed a median OS of 36.5 months, and more than half of those who had a complete MRD response after the first cycle of blinatumomab were still alive at 5 years, which suggests that the treatment might be able to cure some patients. AEs were seen that were linked to ციტოკინის გამოთავისუფლების სინდრომი (CRS).31 Other studies, like NCT03023878 and NCT03340766, are still looking at blinatumomab in first-line settings and in combination with other treatments.
CD19-targeted treatments have been linked to failure because of the loss of CD19 antigen after treatment. The failure rates for blinatumomab range from 8% to 35%, and for CAR T-უჯრედული თერაპია, they range from 39% to 65%.36-40 We don’t fully understand what causes therapy to fail, but one possibility is immunoediting, in which antigen loss is caused by a T-cell-dependent process called immunoselection, which lets tumour cells get away.41 Lineage switch and epitope loss under therapy pressure have also been suggested as ways for tumours to escape treatment. However, a recent study on epitope loss found that some CD19 isoforms that help CAR T-cells escape were already present at the time of diagnosis. This suggests that combining treatments might be helpful. Another thing that can cause immunotherapy to fail is called “inhibitory T-cell signalling.” In this case, the blocking programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is interesting because it is more common in B-cell ALL cells from patients who don’t respond to blinatumomab and can make CD3 BiTE molecules less effective.43 By making a CD28/PD-L1 BiTE that triggers the CD28 co-stimulatory signal instead of the inhibitory signaling pathway that is usually seen when a T cell binds to a PD-L1-expressing cancer cell, this inhibition could be turned off.43 Dual-targeted CAR T cells are also being looked into as a way to make up for the loss of tumour antigens. This can be done by modifying each T cell with 2 CAR molecules and 2 different binding domains (dual-signaling CAR) or by putting 2 different binding domains on 1 CAR molecule at the same time (TanCAR).
გვერდითი მოვლენები BiTE-სთან და მის მენეჯმენტთან
ბლინატუმომაბის კლინიკურ კვლევებში ყველაზე გავრცელებული AE არის ცხელება, სისხლის თეთრი უჯრედების დაბალი რაოდენობა და დაბალი თრომბოციტების რაოდენობა. ზოგიერთი ყველაზე მნიშვნელოვანი რისკია CRS, ნეიროტოქსიკურობა და ნარკოტიკების შეცდომები. ნეიროტოქსიკურობა ასევე შეიძლება მოხდეს CD19-სპეციფიკური CAR T-უჯრედების მკურნალობაში, მაგრამ ეს შეიძლება არ იყოს CD19-ის გამო. 1/1b ფაზის კვლევის შედეგებმა, რომელიც ჯერ კიდევ მიმდინარეობს CD20/CD3 სამიზნეების შესახებ, აჩვენა, რომ CNS AE მე-3 ხარისხის ან უფრო მაღალი იყო იშვიათი (3% ყველა 3 ხარისხის AE). უმეტეს შემთხვევაში, ბლინატუმომაბის რეაქცია CRS-ზე რბილია, მაგრამ იშვიათ შემთხვევებში ის შეიძლება იყოს მძიმე და სიცოცხლისთვის საშიშიც კი. ანთებითი რეაქციები შეიძლება შემცირდეს კორტიკოსტეროიდებით. CRS-ის რისკის შესამცირებლად უმჯობესია პრედნიზონის ან დექსამეტაზონის ინფუზია ბლინატუმომაბის პირველი დოზის მიღებამდე და დოზის ნელა გაზრდა. კორტიკოსტეროიდების ამ გამოყენებამ სხვა BiTE მოლეკულებამდე მისცა საფუძველი დექსამეტაზონის, როგორც პრემედიკაციის გამოყენებას სხვა BiTE მოლეკულების გამოყენებისას. თუმცა, გაურკვეველია, შეიძლება თუ არა ამ ეფექტის გამოყენება მთელ BiTE პლატფორმაზე და განიხილება CRS-თან გამკლავების სხვა გზები. ინტერლეუკინი 6 არის ციტოკინი, რომელიც იწვევს CRS-ს და მაღალია ადამიანებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ ეს. ტოცილიზუმაბი, რომელიც ბლოკავს ინტერლეიკინ-6 რეცეპტორს, გამოიყენებოდა CRS-ის სამკურნალოდ, რომელიც ძალიან ცუდია CAR T- უჯრედების მკურნალობის შემდეგ.49 საავადმყოფოში სიმსივნის ნეკროზის ფაქტორი-ინჰიბიტორები ასევე გამოიყენებოდა CRS-ის სამკურნალოდ.