Immuno-oncology is a way to treat cancer by using the body’s immune system. BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) technology is a targeted immuno-oncology platform that binds a patient’s own T cells to cancer cells. Because BiTE technology is flexible, it is easy to make molecules that attack tumor-specific antigens, which makes immuno-oncotherapy possible. Blinatumomab was the first standard BiTE molecule to be approved. It targets CD19 surface antigens on B cells and is mostly unaffected by genetic changes or escape mechanisms inside cells. More BiTE molecules are being made to treat other blood cancers (like multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukaemia, and B-cell لنفوم غیر هوچکین) and solid tumours (like prostate cancer, glioblastoma, stomach cancer, and small-cell lung cancer). BiTE molecules that have a longer half-life than the standard ones are also being made. With BiTE technology, advances in immuno-oncology could make it easier to treat both blood and solid tumours and make them more effective when used with other treatments.
BiTe تراپی چیست؟
Immuno-oncology therapies are scientifically proven ways to treat different types of solid and سرطان های خون. Hematologic cancers are a good fit for treatments that target the immune system because cancerous blood cells move around with immune cells. Several ایمن درمانی درمان سرطان در حال انجام است.
Monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitors that stop the binding of checkpoint proteins (like PD-1 and CTLA-4) are useful against many types of cancer. They work well and are safe for many solid tumours, especially when they target PD-1. Non-small-cell lung, kidney, and bladder cancers have all been treated successfully with these drugs. But many people don’t react to checkpoint inhibitors or get sick again after taking them. Except for non-Hodgkin لنفوم, most results on hematologic cancers have been disappointing, especially for myeloma and leukaemia, where the overall response rate in approved indications ranges from 12.0% to 48.5%.8-15.
Other immuno-oncology treatments, on the other hand, have a higher success rate. Chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies change a patient’s T cells to attack a specific cellular antigen, such as CD19 in the treatment of B-cell malignancies and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in the treatment of میلوم چندگانه (MM). CAR T-cell treatments have shown promise in treating hematologic cancers. They haven’t been as effective in treating solid tumours, but there have been some good results with نوروبلاستوما, human epidermal growth factor receptor tumours, and non-small-cell lung cancer. The genetic modification and in vitro multiplication of T cells take a long and complicated manufacturing process. This is a downside of this therapy because it makes it harder for patients to get this treatment quickly and in large numbers. The fact that lymphodepletion through chemotherapy preparation must be done first as a requirement for improved effectiveness is also a drawback.
درمانهای BiTE (درگیرکننده سلولهای T bispecific) سلولهای T خود بیمار را به آنتیژنهای بیانشده تومور مرتبط میکند. این توانایی سیتوتوکسیک سلولهای T خود بیمار را برای کشتن سرطان بدون تغییر ژنهای سلولهای T یا نیاز به رشد یا دستکاری آنها در خارج از بدن فعال میکند. مولکولهای BiTE را میتوان بهتنهایی بهعنوان دارو یا سایر درمانها برای مؤثرتر ساختن آنها استفاده کرد.
مکانیسم اثر BiTe
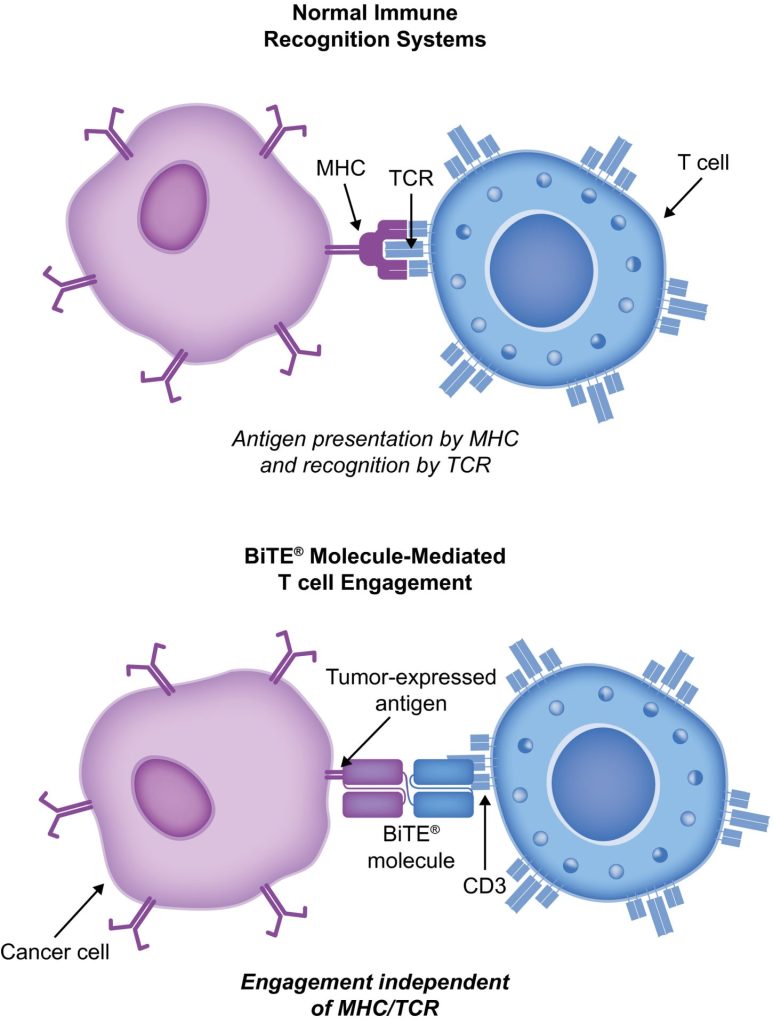
BiTE molecules are antibody constructs with two binding domains. One recognises tumor-expressed antigens (such as BCMA, CD19, or -like protein [DLL3]), and the other, CD3, recognises T cells (Fig. 1). Two single-chain variable fragment (scFv) regions from monoclonal antibodies are connected by a flexible peptide linker to make the binding domains. The first scFv binding region can be changed to target any surface antigen, so it can be used right away to treat a wide range of tumours and can be used again later. The second scFv binding region always binds to CD3, which is a part of the T-cell receptor complex that never changes. When a BiTE molecule interacts with both a cytotoxic T cell and a tumour cell, the T cells begin to multiply. This increases the amount of effector cells and makes BiTE therapy more effective. Then, the death of cancer cells is started. BiTE molecules can get any T cells to do this because they don’t need co-stimulation or the usual processes of the major histocompatibility complex.
Blinatumomab is the first and only BiTE therapy that has been approved. It targets the CD19 receptor on both normal and cancerous B cells. It is a highly potent molecule with cytotoxic effects seen at low exposures (10–100 pg/mL)26. In its presence, T cells can perform serial-target lysis, quickly binding to and killing many cells. This is how BiTE therapies work, and it can be seen in other BiTE molecules that are still in research. In لوسمی لنفوبلاستیک حاد (ALL), blinatumomab has been shown to be effective and safe. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration gave it fast approval, and in 2017, it got full approval for relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL. In 2018, accelerated approval was given to بلیناتوموماب for treating BCP-ALL with minimum residual disease (MRD). This was the first approval for this use. In November 2015, the European Medicines Agency also gave it a green light for BCP-ALL with a Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) that is negative and R/R. Blinatumomab is approved for R/R BCP-ALL in adults and children in 57 countries, including Japan, all countries in the European Union, Canada, and Australia.
Blinatumomab برای درمان بیماران مبتلا به BCP-ALL
Blinatumomab روش درمان BCP-ALL را تغییر داده است. در مقایسه با شیمی درمانی استاندارد مراقبت (SOC)، بقای کلی (OS) را افزایش داده و تعداد عوارض جانبی خاص (AEs) را کاهش داده است. چندین مطالعه مهم، از جمله کارآزماییهای تصادفیسازی و کنترلشده، نشان داد که بلیناتوماب بیخطر است و برای BCP-ALL در بزرگسالان و کودکان کار میکند. سلول درمانی T با CARتنها اطلاعاتی از 2 مطالعه تک بازویی (clinicaltrials.gov ID NCT01626495 و NCT01029366) وجود دارد که در آن 25 کودک (سنین 5 تا 22 سال) و 5 بزرگسال (سن 26 تا 60 سال) با R/R BCP-ALL و ALL سلول T تحت درمان قرار گرفتند. اما نتایج امیدوارکننده هستند (پاسخ کامل [CR] در 90٪، بهبودی پایدار با بقای 6 ماهه بدون رویداد در 67٪، و نرخ بقای کلی [OS] 78٪ [متوسط پیگیری، 7 ماه؛ محدوده، 1-24 ماه]).
مطالعه TOWER (مطالعه فاز 3، تصادفی شده، مطالعه برچسب باز بررسی اثربخشی آنتی بادی BiTE Blinatumomab در مقابل استاندارد مراقبت از شیمی درمانی در افراد بالغ با پیش ساز B عودکننده/نسوز ALL؛ با شناسه کلینیکی آزمایشات gov. s با Ph منفی، R/R BCP-ALL. از آنجایی که مردم عمر طولانی تری داشتند، مطالعه زودتر متوقف شد. AEها در گروه بلیناتوموماب مشابه آنچه در مطالعات قبلی مشاهده شده بود، بود و بلیناتوماب نسبت به SOC دارای میزان AE تنظیم شده با قرار گرفتن در معرض کمتری بود.
30% to 50% of people with BCP-ALL in complete hematologic remission show persistent MRD. In the single-arm, phase 2 BLAST study (A Confirmatory Multicenter, Single-Arm Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of the BiTE Antibody Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With MRD of B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia; clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01207388), blinatumomab was tested on patients with BCP-ALL in first or later complete After blinatumomab treatment, 78% of patients who were MRD positive became MRD negative. The 5-year OS study showed a median OS of 36.5 months, and more than half of those who had a complete MRD response after the first cycle of blinatumomab were still alive at 5 years, which suggests that the treatment might be able to cure some patients. AEs were seen that were linked to سندرم رهش سیتوکین (CRS).31 Other studies, like NCT03023878 and NCT03340766, are still looking at blinatumomab in first-line settings and in combination with other treatments.
CD19-targeted treatments have been linked to failure because of the loss of CD19 antigen after treatment. The failure rates for blinatumomab range from 8% to 35%, and for درمان با سلول T CAR, they range from 39% to 65%.36-40 We don’t fully understand what causes therapy to fail, but one possibility is immunoediting, in which antigen loss is caused by a T-cell-dependent process called immunoselection, which lets tumour cells get away.41 Lineage switch and epitope loss under therapy pressure have also been suggested as ways for tumours to escape treatment. However, a recent study on epitope loss found that some CD19 isoforms that help CAR T-cells escape were already present at the time of diagnosis. This suggests that combining treatments might be helpful. Another thing that can cause immunotherapy to fail is called “inhibitory T-cell signalling.” In this case, the blocking programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is interesting because it is more common in B-cell ALL cells from patients who don’t respond to blinatumomab and can make CD3 BiTE molecules less effective.43 By making a CD28/PD-L1 BiTE that triggers the CD28 co-stimulatory signal instead of the inhibitory signaling pathway that is usually seen when a T cell binds to a PD-L1-expressing cancer cell, this inhibition could be turned off.43 Dual-targeted CAR T cells are also being looked into as a way to make up for the loss of tumour antigens. This can be done by modifying each T cell with 2 CAR molecules and 2 different binding domains (dual-signaling CAR) or by putting 2 different binding domains on 1 CAR molecule at the same time (TanCAR).
رویدادهای نامطلوب با BiTE و مدیریت آن
در مطالعات بالینی بلیناتوماب، شایع ترین AE ها تب، تعداد گلبول های سفید خون و تعداد پلاکت پایین است. برخی از مهمترین خطرات عبارتند از CRS، سمیت عصبی و اشتباهات دارویی. سمیت عصبی همچنین میتواند با درمانهای سلول T CAR اختصاصی CD19 رخ دهد، اما ممکن است به دلیل CD19 نباشد. نتایج یک مطالعه فاز 1/1b که هنوز در مورد اهداف CD20/CD3 ادامه دارد، نشان داد که AEهای CNS درجه 3 یا بالاتر نادر بودند (3٪ از تمام AEهای درجه 3). اغلب اوقات، واکنش بلیناتوماب به CRS خفیف است، اما در موارد نادر، می تواند شدید و حتی تهدید کننده زندگی باشد. واکنش های التهابی را می توان با کورتیکواستروئیدها کاهش داد. برای کاهش احتمال CRS، بهتر است قبل از اولین دوز بلیناتوماب انفوزیون پردنیزون یا دگزامتازون داده شود و دوز به آرامی افزایش یابد. این استفاده از کورتیکواستروئیدها قبل از سایر مولکول های BiTE دلیلی برای استفاده از دگزامتازون به عنوان پیش دارو در هنگام استفاده از سایر مولکول های BiTE ایجاد کرده است. با این حال، مشخص نیست که آیا این اثر می تواند در کل پلتفرم BiTE اعمال شود یا خیر، و راه های دیگری برای مقابله با CRS در حال بررسی است. اینترلوکین 6 یک سیتوکین است که باعث CRS می شود و در افرادی که آن را دارند بسیار زیاد است. توسیلیزوماب، که گیرنده اینترلوکین 6 را مسدود می کند، برای درمان CRS که پس از درمان با سلول T CAR بسیار بد است، استفاده شده است.