CAR T cell therapy is a new and potentially effective way to treat some types of cancer, especially blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphoma. But it is also known for being expensive. The cost of CAR T cell treatment depends on a number of things, such as the type of therapy used, the type of cancer being treated, and the country’s health care system.
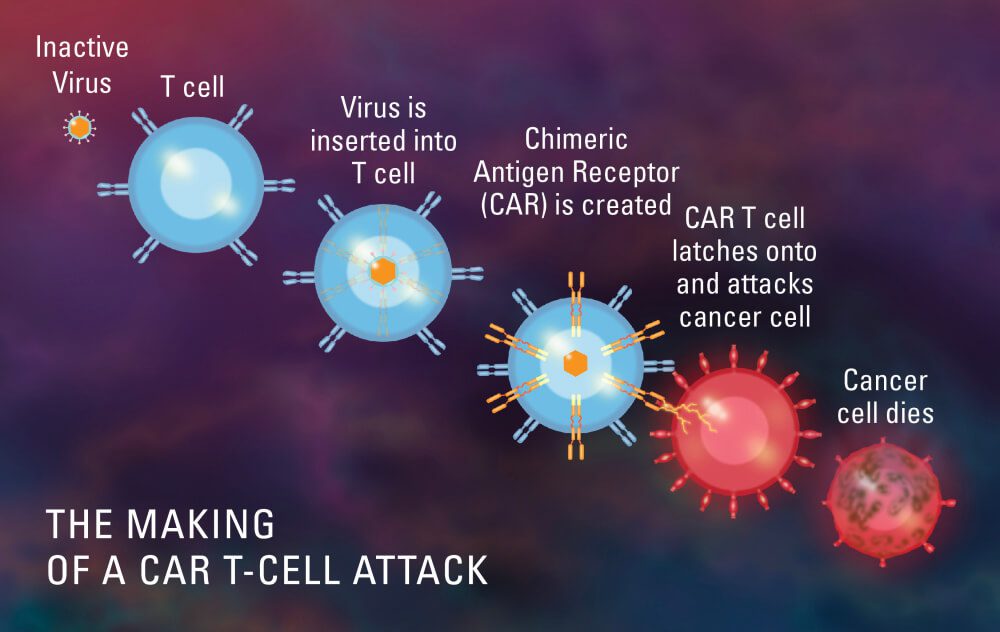
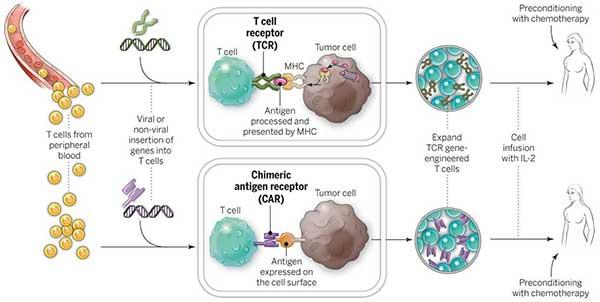
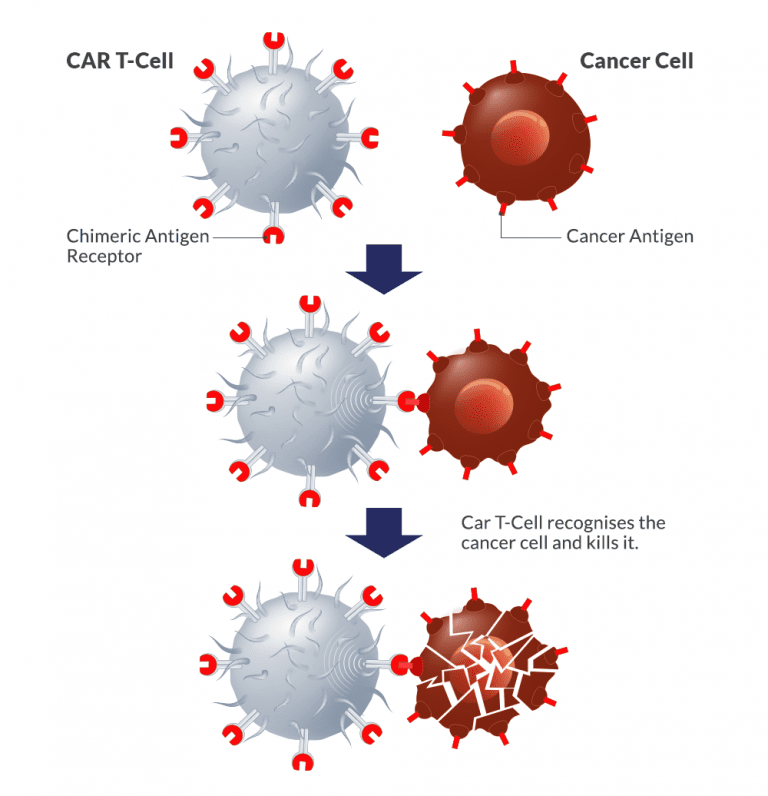
In general, CAR T cell therapy is a complicated process that involves taking a patient’s own immune cells, changing them in a lab to make them express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), and then putting them back into the patient to target and kill cancer cells. From collecting the cells to giving them back to the patient, the whole process needs specialised facilities, skilled medical professionals, and cutting-edge technology, all of which add to the high cost.
CAR T cell therapy can cost anywhere from tens of thousands of dollars to millions of dollars per treatment. This includes not only the costs of the therapy itself, but also the costs of pre-treatment tests, hospitalisation, tracking, and dealing with any possible side effects. Also, some patients may need more than one dose of CAR T cell therapy, which would add to the total cost.
Even though the high cost of CAR T cell therapy makes it hard for patients and healthcare systems to pay for, it is important to remember that ongoing study and progress in the field are working to make this treatment easier to get and less expensive. People are working to simplify the manufacturing process, cut costs, and look into alternative payment models to make this groundbreaking treatment more affordable and give more people access to it.
Cost of CAR T-Cell therapy in different countries:
USA – $ 500,000 – 700,000 USD
Israel – $ 75,000 – 100,000 USD
China – $ 60,000 – 80,000 USD
UK – $ 500,000 – 700,000 USD
Singapore – $ 500,000 – 700,000 USD
Australia – $ 500,000 – 700,000 USD
South-Korea – $ 500,000 – 700,000 USD
Japan – $ 500,000 – 700,000 USD