Survivorship and long-term care in advanced cancers
Understanding Survivorship in the Context of Advanced Cancers
Survivorship, once a term associated predominantly with those in remission, has evolved. Today, it encompasses a multifaceted journey that includes individuals living with advanced cancers. In this ever-shifting paradigm, we delve into the nuances of survival beyond the initial diagnosis and treatment phase.
- The definition and scope of survivorship care
- Impact of chronic management of advanced cancers
- The importance of comprehensive survivorship programs
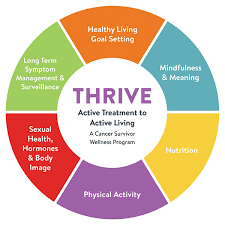
The Landscape of Long-Term Care for Advanced Cancer Patients
Navigating the healthcare ecosystem for advanced cancer care presents its own set of challenges. From the intricacies of palliative care options to the logistics of care coordination, we explore the current state of long-term care and its impact on patients’ quality of life.
- Palliative care vs. aggressive treatment in advanced stages
- Accessibility and affordability of long-term care services
- Innovations in treatment that are changing the landscape
Navigating the Emotional and Psychological Journey
The odyssey of living with advanced cancer is not solely a physical battle; it is equally a psychological and emotional one. Here, we shine a light on the internal struggles and the resilience of the human spirit, as well as the support systems that bolster survivors along the way.
- The role of psychosocial support in survivorship
- Strategies for managing the emotional toll of advanced cancer
- The importance of community and support networks
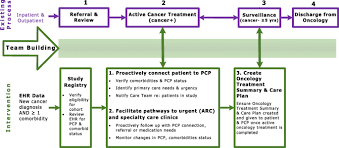
The Future of Care Coordination and Survivorship Plans
As we cast our gaze towards the horizon, the future of survivorship and long-term care in advanced cancers is one of hope, innovation, and patient-centered care. This final act discusses the forward momentum in the field and what it means for survivors.
- Emerging trends in survivorship care planning
- The integration of technology in long-term care management
- The evolving role of healthcare providers in survivorship
FAQ’s
What is survivorship in the context of advanced cancer?
Survivorship in the context of advanced cancer refers to the ongoing experience of individuals living with cancer beyond the initial diagnosis and treatment phases. Unlike in earlier stages, where survival rates are generally higher, advanced cancer (stage 4) often involves treatments aimed at managing symptoms and extending life rather than curing the disease. Survivorship here encompasses coping with physical and emotional challenges, navigating complex treatment decisions, and maintaining quality of life. It’s a period marked by resilience, adapting to new norms, and seeking support from healthcare providers and loved ones. Survivorship in advanced cancer emphasizes living fully despite the disease’s progression.
How has long-term care for advanced cancer patients evolved?
Long-term care for advanced cancer patients has evolved significantly over the years. Initially focused on palliative treatments to manage symptoms and improve quality of life, modern approaches now integrate personalized care plans tailored to each patient’s needs. This evolution includes advancements in pain management, targeted therapies, and psychosocial support. Additionally, holistic approaches encompass nutritional guidance, exercise programs, and integrative therapies to address physical and emotional well-being. Long-term care also emphasizes shared decision-making, empowering patients with treatment choices. Furthermore, advancements in telemedicine enable remote monitoring and support, enhancing accessibility and continuity of care for advanced cancer patients.
What are the key components of a survivorship care plan?
A survivorship care plan typically includes key components essential for comprehensive post-treatment support. Firstly, it outlines the patient’s diagnosis, treatments received, and potential long-term effects. Secondly, it details a schedule for follow-up appointments, monitoring, and necessary screenings. Thirdly, it addresses specific concerns related to physical, emotional, and psychosocial well-being, including symptom management and lifestyle recommendations. Fourthly, it provides information on resources and support services available, such as support groups or counseling. Lastly, it encourages active communication between the patient, caregivers, and healthcare team. This plan aims to empower survivors by promoting awareness, self-care, and a proactive approach to long-term health management.
What role do primary care providers play in long-term cancer care?
Primary care providers play a crucial role in long-term cancer care by offering comprehensive and continuous support beyond initial treatment. They monitor survivors for cancer recurrence, manage treatment side effects, and address overall health needs. Primary care providers coordinate follow-up care, conducting regular screenings for secondary cancers and other health issues. They also collaborate with oncologists and specialists to optimize survivorship care plans, ensuring holistic management of physical and psychosocial aspects. Moreover, primary care providers educate survivors on healthy lifestyles, offer preventive care, and provide emotional support throughout the survivorship journey, fostering a patient-centered approach to long-term cancer care.
How do treatment advances impact survivorship in advanced cancer?
Treatment advances have a significant impact on survivorship in advanced cancer by extending life expectancy and improving quality of life. Targeted therapies and immunotherapies offer tailored approaches, targeting specific cancer markers and enhancing treatment effectiveness with fewer side effects. Advances in pain management and supportive care alleviate symptoms, enhancing comfort and well-being. Precision medicine allows for personalized treatment plans, optimizing outcomes. Additionally, clinical trials provide access to innovative therapies, expanding treatment options. These advancements empower patients with advanced cancer to navigate their disease more effectively, fostering hope and resilience. Overall, treatment advances enhance survivorship by prolonging life and enhancing the overall quality of life for patients with advanced cancer.
What are the emotional and psychological aspects of cancer survivorship?
Cancer survivorship encompasses complex emotional and psychological aspects. Patients often experience a range of emotions, including fear of recurrence, anxiety, depression, and uncertainty about the future. Coping with physical changes, treatment side effects, and lifestyle adjustments can also impact emotional well-being. Survivorship brings unique challenges like adjusting to a “new normal,” managing survivor guilt, and navigating relationships. However, many survivors find strength in resilience, developing post-traumatic growth, and a deeper appreciation for life. Support from loved ones, counseling, support groups, and mindfulness practices play vital roles in addressing these emotional and psychological aspects, fostering healing and emotional stability post-cancer.
How can caregivers support long-term, advanced cancer care?
Caregivers play a crucial role in supporting long-term, advanced cancer care by providing physical, emotional, and practical assistance to patients. They offer companionship and advocacy during medical appointments, ensuring patients understand treatment options and adhere to care plans. Caregivers assist with daily activities, medication management, and symptom monitoring, enhancing patient comfort and quality of life. Emotional support is key, as caregivers offer empathy, reassurance, and a listening ear during challenging times. Respite care allows caregivers to recharge. They also facilitate communication among healthcare providers and family members, ensuring a cohesive support network. Ultimately, caregivers provide essential holistic support, enhancing the overall well-being of patients with advanced cancer.
What are the challenges of coordinating care for advanced cancer survivors?
Coordinating care for advanced cancer survivors presents several challenges. Firstly, survivors often require complex, multidisciplinary care involving oncologists, primary care providers, specialists, and supportive services. Ensuring seamless communication and collaboration among these diverse healthcare professionals can be challenging. Secondly, managing survivorship care plans tailored to individual needs and addressing ongoing treatment, surveillance, and symptom management requires careful coordination. Thirdly, survivors may face financial, logistical, or geographic barriers to accessing necessary services and follow-up care. Lastly, addressing psychosocial needs and providing adequate emotional support adds another layer of complexity. Overcoming these challenges requires a patient-centered approach, effective communication, and comprehensive care coordination strategies.
How does quality of life factor into survivorship and long-term care?
Quality of life is a critical factor in survivorship and long-term care for cancer patients. It encompasses physical, emotional, social, and functional well-being. Enhancing quality of life involves managing symptoms, minimizing treatment side effects, and promoting overall wellness. Addressing psychosocial needs, such as anxiety, depression, and survivorship guilt, is essential. Supporting patients in maintaining meaningful relationships and engaging in enjoyable activities contributes to a higher quality of life. Empowering patients to make informed decisions, offering support services, and encouraging healthy lifestyle behaviors also play key roles. Ultimately, prioritizing quality of life enhances survivorship outcomes and promotes holistic well-being throughout the cancer journey.
What resources are available for advanced cancer survivors and their families?
Advanced cancer survivors and their families have access to a range of resources to support them through their journey. Medical institutions often provide survivorship programs offering specialized care plans, follow-up services, and support groups. Palliative care teams assist in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Community organizations offer counseling, financial assistance, and transportation services. Online platforms and helplines provide educational resources and connect individuals with peer support networks. Social workers and navigators help coordinate care and access to available resources. Hospice care is available for end-of-life support. Overall, a comprehensive network of resources exists to support advanced cancer survivors and their families in various aspects of care and well-being.
Susan Hau is a distinguished researcher in the field of cancer cell therapy, with a particular focus on T cell-based approaches and cancer vaccines. Her work spans several innovative treatment modalities, including CAR T-cell therapy, TIL (Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte) therapy, and NK (Natural Killer) cell therapy.
Hau's expertise lies in cancer cell biology, where she has made significant contributions to understanding the complex interactions between immune cells and tumors.
Her research aims to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapies by manipulating the tumor microenvironment and exploring novel ways to activate and direct immune responses against cancer cells.
Throughout her career, Hau has collaborated with leading professors and researchers in the field of cancer treatment, both in the United States and China.
These international experiences have broadened her perspective and contributed to her innovative approach to cancer therapy development.
Hau's work is particularly focused on addressing the challenges of treating advanced and metastatic cancers. She has been involved in clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of various immunotherapy approaches, including the promising Gamma Delta T cell therapy.
- Comments Closed
- April 24th, 2024





Advanced cancer long-term management, Cancer survivorship care, Chronic cancer management, Late-stage cancer recovery, Palliative care integration, Post-treatment monitoring, Quality of life in survivors, Survivorship care plans
Welcome to CancerFax!
"CancerFax connects patients with advanced cancer treatments in China and India. They specialize in cellular therapies like CAR-T, TIL, and NK, along with stem cell transplants."
Our focus is on providing personalized options and facilitating access to cutting-edge clinical trials.
Ref: Survivorship and long-term care in advanced cancers
Chat to know more>