Introduction
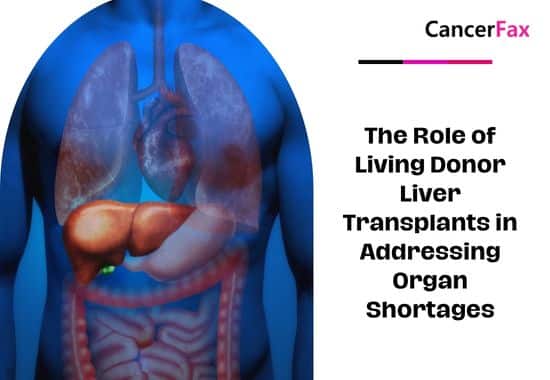
Liver transplant is a life-saving operation for end-stage liver disease, acute liver failure, or some metabolic disorders. But demand for liver transplantation far outweighs the supply of deceased donor organs. Under these conditions, living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) has become an important option, especially in regions like India, where the cadaveric organ waiting list keeps rising.
The Growing Need for Liver Transplants in India
India has experienced a sharp surge in liver illness caused by factors like alcohol abuse, hepatitis infections, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Consequently, the need for liver transplants has grown at an exponential rate. Nevertheless, deceased donor livers are scarce because organ donation rates are low and there are problems with logistics in organ recovery and allocation.
This deficiency has resulted in the growing dependence on LDLT, where a healthy donor voluntarily gives a section of their liver to the recipient. Due to the liver’s special capacity to regenerate, both the recipient and donor are able to regain full liver function after months of surgery.
Advantages of Living Donor Liver Transplants
- Reduced Waiting Time: One of the biggest challenges for patients requiring a liver transplant in India is the long waiting time for a deceased donor organ. LDLT eliminates this uncertainty, allowing timely intervention.
- Better Organ Quality: Since the organ is retrieved from a healthy, living donor, it is of superior quality compared to a cadaveric liver, which may have experienced ischemic damage.
- Improved Success Rates: The liver transplant success rate in India for LDLT is generally higher due to the planned nature of the surgery and shorter ischemia time.
- Flexibility in Surgery Scheduling: Unlike deceased donor transplants, where the timing is unpredictable, LDLT allows for a well-planned surgery, optimizing both donor and recipient outcomes.
Challenges in Living Donor Liver Transplantation
Although LDLT has some advantages, it has challenges. Both the recipient and donor have major surgery with inherent risks like bleeding, infection, and bile leakage. Ethical issues also crop up with regards to selection of donors, coercion, and postoperative complications. Ensuring proper medical and psychological assessment of donors is essential in order to keep ethical standards intact and risks minimal.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Organ donation and transplantation in India are governed by the Transplantation of Human Organs Act (THOA), 1994, which is responsible for ensuring ethical donation and preventing organ trafficking. According to the act, living donors should be close relatives or should have an altruistic intention, confirmed by an authorization committee. Organ trade is still illegal but a problem and thus deserves regular monitoring and health education campaigns.
The Future of Living Donor Liver Transplants
With advancing medical technology, the future of LDLT is hopeful. Advances in minimally invasive donor hepatectomy, 3D liver perfusion modeling, and regenerative medicine can further promote safety and outcome. Moreover, raising awareness on organ donation and encouraging donors in an ethical way can fill up the gap between organ shortage and demand.
Conclusion
Liver donor transplants are now an indispensable answer to India’s increasing demand for liver transplantation. With great success rates, reduced waiting times, and enhanced outcomes, LDLT is transforming liver transplant programs. Nevertheless, issues of funding, risks to donors, and ethical considerations must be continually confronted to maintain long-term viability for this life-altering procedure. Greater public sensitization and augmentation of the health infrastructure will play a significant role in enhancing accessibility of LDLT to potential candidates.
India’s affordability and state-of-the-art medical facilities have made it a popular destination for liver transplants. If you are planning a liver transplant in India, then it is crucial to select the best hospital for liver transplant in India and be thoroughly informed about the cost of liver transplant in India in order to make sound judgments. Top hospitals for liver transplants in India use the latest medicines and technologies to perform the procedure. Probably this is the reason; the liver transplant success rate in India is more than 80%.



Deceased Donor Liver Transplant, Liver Disease Management, Liver Regeneration, Liver Transplant Success Rates, Living Donor Liver Transplant, Organ Donation Ethics, Organ Shortage, Transplant Waiting Lists
CancerFax is the most trusted online platform dedicated to connecting individuals facing advanced-stage cancer with groundbreaking cell therapies.
Send your medical reports and get a free analysis.
🌟 Join us in the fight against cancer! 🌟
Привет,
CancerFax — это самая надежная онлайн-платформа, призванная предоставить людям, столкнувшимся с раком на поздних стадиях, доступ к революционным клеточным методам лечения.
Отправьте свои медицинские заключения и получите бесплатный анализ.
🌟 Присоединяйтесь к нам в борьбе с раком! 🌟