CAR T-Cell Therapy In Turkey
Planning to visit Turkey for CAR T treatment?
Get an estimate from the top hospitals in Turkey.
CAR T cell therapy is emerging in Turkey’s healthcare landscape, offering new hope for patients with certain blood cancers. This innovative treatment involves modifying a patient’s immune cells to target cancer cells effectively. While still developing, Turkish medical centers are exploring CAR T cell therapy’s feasibility and effectiveness. Challenges like cost and infrastructure exist, but ongoing research and collaborations suggest a growing interest in adopting this promising therapy to enhance cancer care in Turkey.
CAR-T therapy is a novel form of cancer treatment that uses the immune system to eradicate cancer cells. Where other therapies have failed, it has occasionally been able to heal patients. This blog will highlight all that you need to know about this procedure. Read on to find out more!
What is CAR-T Cell therapy?
This type of therapy involves modifying the patient’s T cells, an immune cell type, in the lab so they will bind to and kill cancer cells. A tube transports blood from a vein in the patient’s arm to an apheresis device (not shown), which extracts white blood cells, including T cells, and returns the remaining blood to the patient.
The T cells are then genetically modified in the lab to contain the gene for a unique receptor known as a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). The CAR T cells are multiplied in a lab before being infused into the patient in large numbers. The antigen on the cancer cells can be recognized by CAR T cells, which then kill the cancer cells.
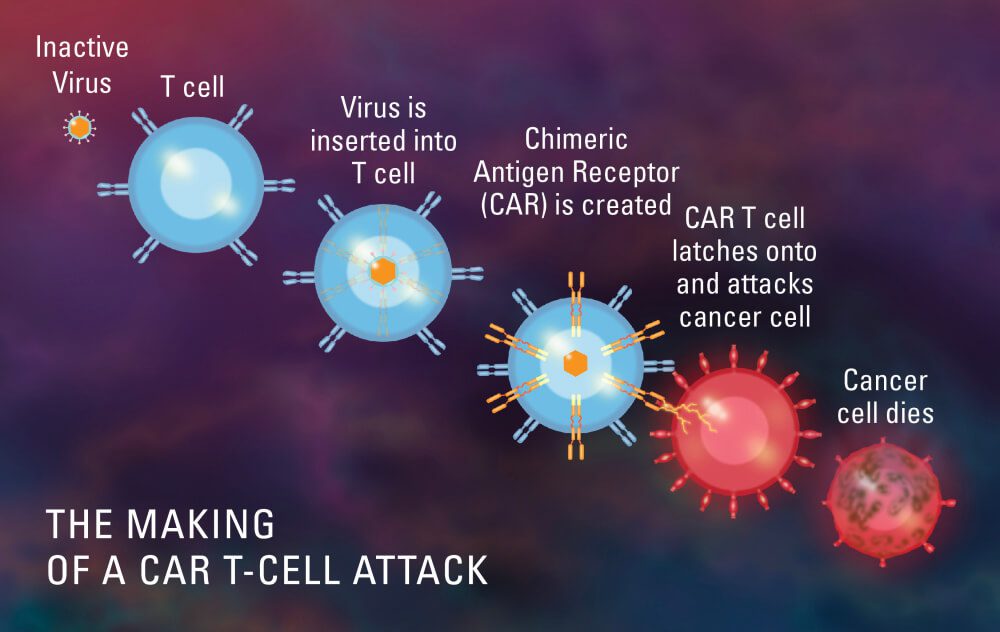
What is the procedure for CAR-T Cell therapy?
The CAR-T therapy procedure, which takes a few weeks, involves multiple steps:
T cells are extracted from your blood using a tube that is placed into an arm vein. This takes a couple of hours.
T cells are transported to a facility where they undergo genetic modification to become CAR-T cells. Two to three weeks pass throughout this.
CAR-T cells are reintroduced into your bloodstream through a drip. This requires several hours.
CAR-T cells target and eliminate cancer cells throughout the body. After receiving CAR-T therapy, you will be closely watched.
What are the side effects of CAR-T Cell therapy?
Cytokine release syndrome, or CRS, is the typical CAR T-cell side effect. Another name for it is “cytokine storm.” It is experienced by roughly 70–90% of patients, but it only lasts for five to seven days. The majority of people compare it to having a bad flu infection, complete with a high fever, exhaustion, and bodily aches.
The second or third day following the infusion is typically when it begins. It occurs due to the body’s immune system reacting to the T cells’ proliferation and attack on the malignancy.
CRES, which stands for CAR T-cell-related encephalopathy syndrome, is the other adverse impact. Around day five following the infusion, it usually begins. Patients may have confusion and disorientation, and occasionally they may be unable to talk for several days.
Although CRES is reversible and normally lasts between two and four days, it can be stressful for patients and their families. All neurological functions gradually return to normal in patients.
What type of cancer cells can be treated with CAR-T Cell Therapy?
Only patients with adult B-cell non-lymphoma Hodgkin’s or pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia who have already tried two unsuccessful conventional therapies can currently use CAR T-cell therapy products that have received FDA approval. However, CAR T-cell therapy is now being tested in clinical studies as a first or second-line treatment for adult lymphoma and pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
What are the advantages of CAR-T Cell therapy?
The main benefit is that CAR T-cell therapy only requires a single infusion and often only requires two weeks of inpatient care. Patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma and pediatric leukemia who have just been diagnosed, on the other hand, typically need chemotherapy for at least six months or more.
The advantages of CAR T-cell therapy, which is actually a living medication, can persist for many years. If and when a relapse occurs, the cells will still be able to identify and target cancer cells because they can survive in the body for an extended period of time.
Although the information is still developing, 42% of adult lymphoma patients who underwent CD19 CAR T-cell treatment were still in remission after 15 months. And after six months, two-thirds of patients with pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia were still in remission. Unfortunately, these patients had exceedingly aggressive tumors that weren’t successfully treated using traditional standards of care.
What type of patients would be good recipients of the CAR-T Cell Therapy?
The optimum candidate for CAR T-cell therapy at this time is a juvenile with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or an adult with severe B-cell lymphoma who has already had two lines of ineffective therapy.
Before the end of 2017, there was no accepted standard of care for patients who had already gone through two lines of therapy without experiencing remission. The only FDA-approved treatment that has so far proven to be significantly beneficial for these patients is CAR T-cell therapy.
What is the scope of CAR-T Cell therapy in Turkey?
A pilot clinical trial (NCT04206943) designed to assess the safety and feasibility of ISIKOK-19 T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed and refractory CD19+ tumors was conducted and participating patients received ISIKOK-19 infusions between October 2019 and July 2021. Production data of the first 8 patients and the clinical outcome of 7 patients who received ISIKOK-19 cell infusion is presented in this study.
Results: Nine patients were enrolled for the trial (ALL n=5 and NHL n=4) but only 7 patients could receive the treatment. Two out of three ALL patients and three out of four NHL patients had complete/partial response (ORR 72%). Four patients (57%) had CAR-T-related toxicities (CRS, CRES, and pancytopenia). Two patients were unresponsive and had progressive disease following CAR-T therapy. Two patients with partial response had progressive disease during
follow-up.
Conclusion: Production efficacy and fulfilling the criteria of quality control were satisfactory for academic production. Response rates and toxicity profiles are acceptable for this heavily pretreated/refractory patient group. ISIKOK-19 cells appear to be a safe, economical, and efficient treatment option for CD19 positive tumors. The findings of this study need to be
supported by the currently ongoing clinical trial of ISIKOK-19.
To Conclude
This represents a significant advancement in the management of leukemia and B-cell lymphoma. Additionally, it gives hope to those whose lives had previously been predicted to last only six months. Now that we have identified mechanisms of resistance and created more techniques to combat them, the future appears to be much more promising.
For more details on CAR-T Cell Therapy in Turkey, head over to our website. Get in touch with our highly experienced healthcare providers here at CancerFax for a free consultation to work out a suitable care plan for your healthcare needs!

Image: One of the hospital in Turkey where CAR T Cell therapy trials were conducted.