Immuno-oncology is a way to treat cancer by using the body’s immune system. BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) technology is a targeted immuno-oncology platform that binds a patient’s own T cells to cancer cells. Because BiTE technology is flexible, it is easy to make molecules that attack tumor-specific antigens, which makes immuno-oncotherapy possible. Blinatumomab was the first standard BiTE molecule to be approved. It targets CD19 surface antigens on B cells and is mostly unaffected by genetic changes or escape mechanisms inside cells. More BiTE molecules are being made to treat other blood cancers (like multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukaemia, and B-cell نان ہڈکن لیمفا) and solid tumours (like prostate cancer, glioblastoma, stomach cancer, and small-cell lung cancer). BiTE molecules that have a longer half-life than the standard ones are also being made. With BiTE technology, advances in immuno-oncology could make it easier to treat both blood and solid tumours and make them more effective when used with other treatments.
BiTe تھراپی کیا ہے؟
Immuno-oncology therapies are scientifically proven ways to treat different types of solid and خون کے کینسر. Hematologic cancers are a good fit for treatments that target the immune system because cancerous blood cells move around with immune cells. Several immunotherapy کی کینسر کے علاج پر کام جاری ہے۔
Monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitors that stop the binding of checkpoint proteins (like PD-1 and CTLA-4) are useful against many types of cancer. They work well and are safe for many solid tumours, especially when they target PD-1. Non-small-cell lung, kidney, and bladder cancers have all been treated successfully with these drugs. But many people don’t react to checkpoint inhibitors or get sick again after taking them. Except for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, most results on hematologic cancers have been disappointing, especially for myeloma and leukaemia, where the overall response rate in approved indications ranges from 12.0% to 48.5%.8-15.
Other immuno-oncology treatments, on the other hand, have a higher success rate. Chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies change a patient’s T cells to attack a specific cellular antigen, such as CD19 in the treatment of B-cell malignancies and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in the treatment of ایک سے زیادہ myeloma (MM). CAR T-cell treatments have shown promise in treating hematologic cancers. They haven’t been as effective in treating solid tumours, but there have been some good results with نیوروبلاسٹوما, human epidermal growth factor receptor tumours, and non-small-cell lung cancer. The genetic modification and in vitro multiplication of T cells take a long and complicated manufacturing process. This is a downside of this therapy because it makes it harder for patients to get this treatment quickly and in large numbers. The fact that lymphodepletion through chemotherapy preparation must be done first as a requirement for improved effectiveness is also a drawback.
BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) علاج مریض کے اپنے T خلیات کو ٹیومر کے اظہار والے اینٹیجنز سے جوڑتا ہے۔ یہ مریض کے اپنے T خلیات کی سائٹوٹوکسک صلاحیت کو چالو کر دیتا ہے کہ وہ T خلیات کے جینز کو تبدیل کیے بغیر یا انہیں جسم سے باہر بڑھنے یا ان میں ہیرا پھیری کی ضرورت کے بغیر کینسر کو مار سکتا ہے۔ BITE مالیکیولز کو اکیلے دواؤں کے طور پر یا دیگر علاج کے ساتھ استعمال کیا جا سکتا ہے تاکہ انہیں زیادہ موثر بنایا جا سکے۔
کارروائی کا BiTe میکانزم
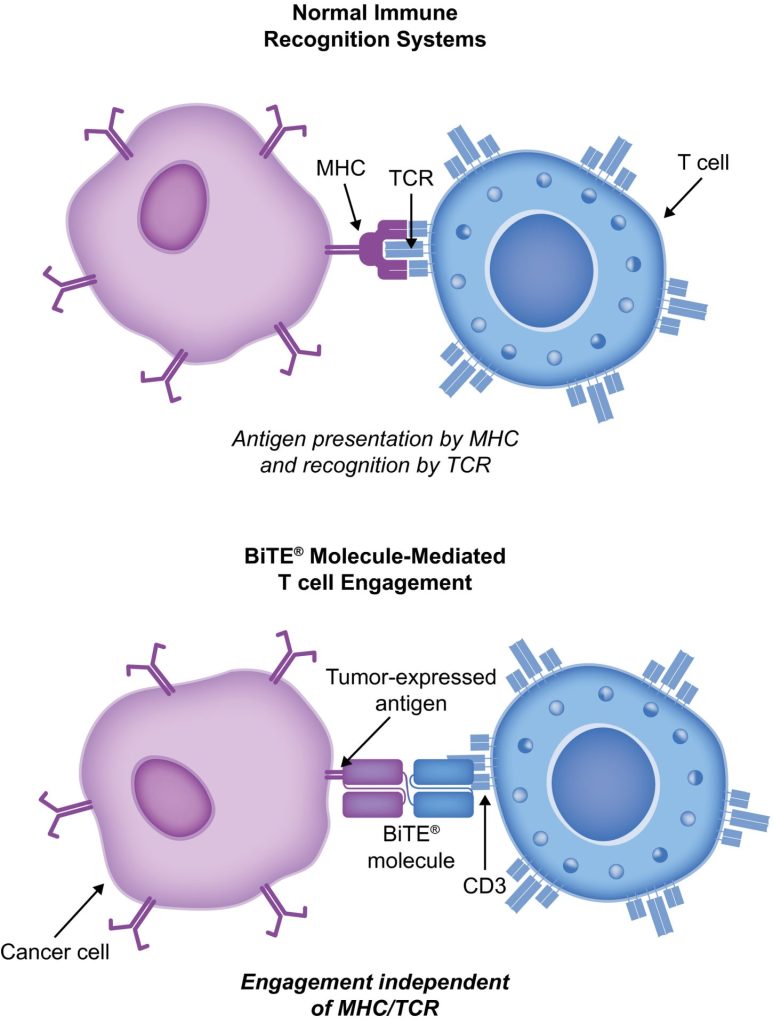
BiTE molecules are antibody constructs with two binding domains. One recognises tumor-expressed antigens (such as بی سی ایم اے, CD19, or -like protein [DLL3]), and the other, CD3, recognises T cells (Fig. 1). Two single-chain variable fragment (scFv) regions from monoclonal antibodies are connected by a flexible peptide linker to make the binding domains. The first scFv binding region can be changed to target any surface antigen, so it can be used right away to treat a wide range of tumours and can be used again later. The second scFv binding region always binds to CD3, which is a part of the T-cell receptor complex that never changes. When a BiTE molecule interacts with both a cytotoxic T cell and a tumour cell, the T cells begin to multiply. This increases the amount of effector cells and makes BiTE therapy more effective. Then, the death of cancer cells is started. BiTE molecules can get any T cells to do this because they don’t need co-stimulation or the usual processes of the major histocompatibility complex.
Blinatumomab is the first and only BiTE therapy that has been approved. It targets the CD19 receptor on both normal and cancerous B cells. It is a highly potent molecule with cytotoxic effects seen at low exposures (10–100 pg/mL)26. In its presence, T cells can perform serial-target lysis, quickly binding to and killing many cells. This is how BiTE therapies work, and it can be seen in other BiTE molecules that are still in research. In شدید لمفوبلاسٹک لیوکیمیا (تمام), blinatumomab has been shown to be effective and safe. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration gave it fast approval, and in 2017, it got full approval for relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL. In 2018, accelerated approval was given to blinatumomab for treating BCP-ALL with minimum residual disease (MRD). This was the first approval for this use. In November 2015, the European Medicines Agency also gave it a green light for BCP-ALL with a Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) that is negative and R/R. Blinatumomab is approved for R/R BCP-ALL in adults and children in 57 countries, including Japan, all countries in the European Union, Canada, and Australia.
BCP-ALL والے مریضوں کے علاج کے لیے Blinatumomab
Blinatumomab نے BCP-ALL کے علاج کے طریقے کو تبدیل کر دیا ہے۔ معیاری نگہداشت (SOC) کیموتھراپی کے مقابلے میں، اس نے مجموعی طور پر بقا (OS) میں اضافہ کیا ہے اور بعض ضمنی اثرات (AEs) کی تعداد میں کمی کی ہے۔ بے ترتیب کنٹرول ٹرائلز سمیت کئی اہم مطالعات سے پتہ چلتا ہے کہ blinatumomab محفوظ ہے اور بالغوں اور بچوں دونوں میں BCP-ALL کے لیے کام کرتا ہے۔ کار ٹی سیل تھراپی، صرف 2 سنگل آرم اسٹڈیز (clinicaltrials.gov IDs NCT01626495 اور NCT01029366) کا ڈیٹا موجود ہے جس میں R/R BCP-ALL اور T-cell ALL کے ساتھ 25 بچوں (عمر 5–22) اور 5 بالغ (عمر 26–60) کا علاج کیا گیا تھا۔ لیکن نتائج امید افزا ہیں (90% میں مکمل ردعمل [CR]، 6% میں 67 ماہ کے واقعات سے پاک بقا کے ساتھ مستقل معافی، اور مجموعی طور پر بقا کی شرح [OS] %78 [میڈین فالو اپ، 7 ماہ؛ حد، 1–24 ماہ])۔
TOWER مطالعہ (ایک فیز 3، بے ترتیب، کھلا لیبل اسٹڈی جو BITE Antibody Blinatumomab کی افادیت کی تحقیقات کرتا ہے اسٹینڈرڈ آف کیئر کیموتھراپی کے ساتھ بالغوں کے مضامین میں Relapsed/Refractory B-Precursor ALL؛ clinicaltrials.gov شناخت کنندہ NCT02013167 کے مقابلے میں mototherapy کے اثرات) پی ایچ-نیگیٹو، R/R BCP-ALL والے بالغوں سے پہلے سے علاج کیا جاتا ہے۔ چونکہ لوگ زیادہ لمبے عرصے تک زندہ رہتے تھے، اس لیے مطالعہ جلد روک دیا گیا تھا۔ blinatumomab گروپ میں AEs وہی تھے جو پہلے کے مطالعے میں دیکھے گئے تھے، اور blinatumomab میں SOC کے مقابلے میں کم ایکسپوژر ایڈجسٹ AE کی شرح تھی۔
30% to 50% of people with BCP-ALL in complete hematologic remission show persistent MRD. In the single-arm, phase 2 BLAST study (A Confirmatory Multicenter, Single-Arm Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of the BiTE Antibody Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With MRD of B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia; clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01207388), blinatumomab was tested on patients with BCP-ALL in first or later complete After blinatumomab treatment, 78% of patients who were MRD positive became MRD negative. The 5-year OS study showed a median OS of 36.5 months, and more than half of those who had a complete MRD response after the first cycle of blinatumomab were still alive at 5 years, which suggests that the treatment might be able to cure some patients. AEs were seen that were linked to سائٹوکائن ریلیز سنڈروم (CRS).31 Other studies, like NCT03023878 and NCT03340766, are still looking at blinatumomab in first-line settings and in combination with other treatments.
CD19-targeted treatments have been linked to failure because of the loss of CD19 antigen after treatment. The failure rates for blinatumomab range from 8% to 35%, and for کار ٹی سیل علاج, they range from 39% to 65%.36-40 We don’t fully understand what causes therapy to fail, but one possibility is immunoediting, in which antigen loss is caused by a T-cell-dependent process called immunoselection, which lets tumour cells get away.41 Lineage switch and epitope loss under therapy pressure have also been suggested as ways for tumours to escape treatment. However, a recent study on epitope loss found that some CD19 isoforms that help CAR T-cells escape were already present at the time of diagnosis. This suggests that combining treatments might be helpful. Another thing that can cause immunotherapy to fail is called “inhibitory T-cell signalling.” In this case, the blocking programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is interesting because it is more common in B-cell ALL cells from patients who don’t respond to blinatumomab and can make CD3 BiTE molecules less effective.43 By making a CD28/PD-L1 BiTE that triggers the CD28 co-stimulatory signal instead of the inhibitory signaling pathway that is usually seen when a T cell binds to a PD-L1-expressing cancer cell, this inhibition could be turned off.43 Dual-targeted CAR T cells are also being looked into as a way to make up for the loss of tumour antigens. This can be done by modifying each T cell with 2 CAR molecules and 2 different binding domains (dual-signaling CAR) or by putting 2 different binding domains on 1 CAR molecule at the same time (TanCAR).
BiTE اور اس کے انتظام کے ساتھ منفی واقعات
blinatumomab کے کلینیکل اسٹڈیز میں، سب سے زیادہ عام AEs بخار، کم سفید خون کے خلیوں کی تعداد، اور پلیٹلیٹ کی کم تعداد ہیں۔ کچھ اہم ترین خطرات CRS، نیوروٹوکسائٹی، اور منشیات کی غلطیاں ہیں۔ نیوروٹوکسائٹی CD19 مخصوص CAR T-cell علاج کے ساتھ بھی ہو سکتی ہے، لیکن یہ CD19 کی وجہ سے نہیں ہو سکتا۔ CD1/CD1 اہداف کے بارے میں ابھی تک جاری رہنے والے مرحلے 20/3b مطالعہ کے نتائج سے پتہ چلتا ہے کہ گریڈ 3 یا اس سے زیادہ کے CNS AEs نایاب تھے (تمام گریڈ 3 AEs کا 3%)۔ زیادہ تر وقت، Blinatumomab کا CRS پر ردعمل ہلکا ہوتا ہے، لیکن غیر معمولی معاملات میں، یہ شدید اور جان لیوا بھی ہو سکتا ہے۔ corticosteroids کے ساتھ سوزش کے ردعمل کو کم کیا جا سکتا ہے. CRS کے امکانات کو کم کرنے کے لیے، blinatumomab کی پہلی خوراک سے پہلے prednisone یا dexamethasone کا ادخال دینا اور خوراک کو آہستہ آہستہ بڑھانا بہتر ہے۔ دیگر BiTE مالیکیولز سے پہلے corticosteroids کے اس استعمال نے دیگر BITE مالیکیولز کا استعمال کرتے وقت ڈیکسامیتھاسون کو بطور دوا استعمال کرنے کی ایک وجہ بتائی ہے۔ تاہم، یہ واضح نہیں ہے کہ آیا یہ اثر پورے BITE پلیٹ فارم پر لاگو کیا جا سکتا ہے، اور CRS سے نمٹنے کے دیگر طریقوں پر غور کیا جا رہا ہے۔ Interleukin 6 ایک سائٹوکائن ہے جو CRS کا سبب بنتا ہے اور یہ ان لوگوں میں زیادہ ہوتا ہے جن کو یہ ہوتا ہے۔ Tocilizumab، جو interleukin-6 ریسیپٹر کو روکتا ہے، CRS کے علاج کے لیے استعمال کیا گیا ہے جو CAR T-cell کے علاج کے بعد بہت برا ہے۔