How to choose immunotherapy drugs for colorectal cancer?
Immunotherapy uses drugs to help the body’s own immune system better recognize and destroy cancer cells. Immunotherapy can be used to treat patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor
An important part of the immune system is its ability to protect itself from attacking the body’s normal cells. For this, it uses “checkpoint” proteins on immune cells, which act like switches that need to be turned on (or off) to start the immune response.
Cancer cells sometimes use these checkpoints to stop the immune system from attacking them. However, drugs aimed at these checkpoints have great prospects as cancer treatment methods.
Drugs called checkpoint inhibitors can be used in people whose colorectal cancer cells have tested positive for specific genetic changes, such as high levels of microsatellite instability (MSI-H), or one of the types of mismatch repair (MMR) Genetic changes.
These drugs are used in people whose cancer is still growing after chemotherapy. They may also be used to treat people whose cancer cannot be removed surgically, relapses after treatment (relapse) or has spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
Approved immunotherapy drugs
PD-1 inhibitor approved
Pembrolizumab (Pembrolizumab, Keytruda) and nivolumab (Nivolumab, Opdivo) are drugs that target PD-1, a protein on cells of the immune system called T cells that usually helps Prevent these cells from attacking other cells in the body. By blocking PD-1, these drugs can enhance the immune response to cancer cells.
On May 24, 2017, the US FDA approved the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab (Pembrolizumab, Keytruda) for the treatment of solid tumor patients with microsatellite highly unstable (MSI-H) / mismatch repair defects (dMMR), The tumor types cover 15 different malignant tumors, including colorectal cancer, small cell lung cancer, and cervical cancer.
On August 2, 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nivolumab (Navumab, Opdivo) for the treatment of fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan. Microsatellite with highly unstable (MSI -H) Treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer in adults or children (≥12 years old) or mismatch repair defects (dMMR).
CTLA-4 inhibitor approved
Ipilimumab (Yervoy) is another drug that can enhance the immune response. It cannot be used alone. It needs to be combined with nivolumab, which blocks CTLA-4, which is another protein on T cells.
The successful case of MSI-High (MSI-High) mCRC is the joint use of nivolumab and ipilimumab, which was evaluated in the Phase II CheckMate142 study. The combination therapy showed an ORR (objective response rate) of 49%, and 5 of 119 patients had CR (complete response) and 53 PR (partial response). Most patients (n = 82) had previously received fluorouracil, oxaliplatin and irinotecan. In these patients, ORR was 46%, 3 CRs and 35 PRs.
According to CheckMate-142 data, the FDA approved the combination (Nivolumab + Ipilimumab) for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, including mCRC patients with MSI-H or mismatch repair defects (dMMR), These patients progressed after treatment with fluorouracil, oxaliplatin and irinotecan.
Interpretation of the application of MSI / dMMR in colorectal therapy
MSI refers to the loss of mismatch repair genes caused by DNA methylation or gene mutations, resulting in changes in the length of microsatellite repeat sequences. The study found that MSI-H is an important biomarker for tumors suitable for immunotherapy.
MSI is microsatellite instability, MMR (mismatch repair) refers to gene mismatch repair function. The human mismatch repair gene (MMR gene) can express the corresponding mismatch repair protein after transcription and translation. If the loss of expression of any MMR protein can cause defects in the cell’s mismatch repair function, the base mismatch in the process of DNA replication The loss of repair function leads to accumulation, which leads to the occurrence of microsatellite instability (MSI). About 15% of colorectal cancers are caused by the MSI pathway.
PCR can be used to detect the length of microsatellite sites (microsatellites are tandem repeats of short DNA sequences in the genome of eukaryotes) in tumor cell DNA, and then compared with the corresponding normal cell DNA. With the popularization and application of NGS (Second Generation Sequencing), in addition to traditional immunohistochemistry and PCR detection, microsatellite status can also be detected on the NGS platform. To understand the authoritative NGS genetic testing institutions at home and abroad, please consult 400-626-9916.
In addition, tumor specimens (including surgical specimens and puncture specimens) can also be used for immunohistochemical detection of four mismatched genes, including: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2. As long as any of these four proteins is missing, the tumor belongs to dMMR, which is a defect of mismatch repair function. If all four proteins are positively expressed and the tumor is pMMR, the mismatch repair function is complete.
Genetic testing MSI report analysis
The following picture shows a patient from the Global Oncologist Network who was found to have MSI-H after MSI testing by a domestic genetic testing company (400-626-9916). This patient is very lucky and suitable for immunotherapy.
Another patient on the Global Oncologist Network was tested positively by the US Keruis Gene (400-626-9916), and all four proteins were positive (positive), which means that the patient was pMMR, and was not suitable for the above approved Immunotherapy.
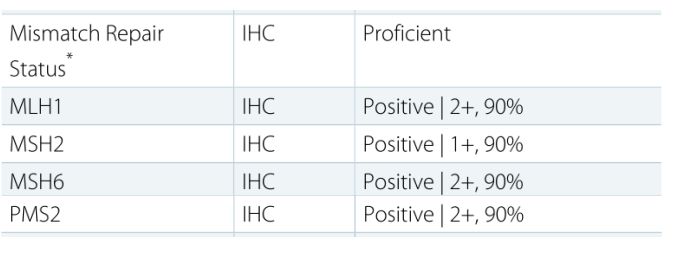
The interpretation of the final test results can be divided into MSS (microsatellite stability), MSI-L (microsatellite low instability) and MSI-H (microsatellite high instability). Generally, dMMR is equivalent to MSI-H, and pMMR is equivalent to MSS and MSI-L.
Precautions for the use of PD-1 inhibitors
- These drugs are given as intravenous (IV) infusions every 2 or 3 weeks.
- Side effects of these drugs include fatigue, cough, nausea, itching, rash, loss of appetite, constipation, joint pain and diarrhea.
- Other more serious side effects occur less frequently. Occasionally, the immune system can attack other parts, possibly causing serious or life-threatening problems in the lungs, intestines, liver, hormone-producing glands, kidneys, or other organs.
- During infusion, the patient’s physical condition needs to be monitored in real time.
Ipilimumab medication precautions
- This medicine is used with nivolumab (Opdivo) to treat colorectal cancer, but it cannot be used alone. It is administered by intravenous (IV) infusion, usually every 3 weeks for 4 cycles of treatment.
- The most common side effects of this medicine include fatigue, diarrhea, rash and itching.
- When using this drug, serious side effects seem to be more common than using PD-1 inhibitors. Like PD-1 inhibitors, this drug can cause the immune system to attack other parts of the body, which can cause serious problems with the gut, liver, hormone-producing glands, nerves, skin, eyes, or other organs. In some people, these side effects can be life-threatening.
- During infusion, the patient’s physical condition needs to be monitored in real time.
How to choose immunotherapy drugs in colorectal cancer?
American colorectal cancer expert Dr. Chiorean said, “Pembrolizumab or nivolumab are more preferred for patients with MSI-H. Nivolumab combined with ipilimumab (CTLA-4 inhibitor) is rarely used. I think the difference i
s very small. Similarly, some people may argue that CTLA-4 may be better tolerated by the inhibitory response, but I also feel that the toxicity is significantly higher. ”
Dr. Messersmith said that when he needed to quickly obtain therapeutic effects, he used nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy. Adding ipilimumab can get an additional 15%–20% response rate. If the patient is symptomatic, it can be added. Even though this may increase adverse reactions, the treatment effect is even greater. This requires an assessment of the patient’s physical condition.
If patients and their families have difficulty in choosing an immunotherapy drug, they can seek domestic authoritative colorectal cancer experts for consultation through the Global Oncologist Network (+91 96 1588 1588) to determine the final, more suitable treatment plan.
Susan Hau is a distinguished researcher in the field of cancer cell therapy, with a particular focus on T cell-based approaches and cancer vaccines. Her work spans several innovative treatment modalities, including CAR T-cell therapy, TIL (Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte) therapy, and NK (Natural Killer) cell therapy.
Hau's expertise lies in cancer cell biology, where she has made significant contributions to understanding the complex interactions between immune cells and tumors.
Her research aims to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapies by manipulating the tumor microenvironment and exploring novel ways to activate and direct immune responses against cancer cells.
Throughout her career, Hau has collaborated with leading professors and researchers in the field of cancer treatment, both in the United States and China.
These international experiences have broadened her perspective and contributed to her innovative approach to cancer therapy development.
Hau's work is particularly focused on addressing the challenges of treating advanced and metastatic cancers. She has been involved in clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of various immunotherapy approaches, including the promising Gamma Delta T cell therapy.
- Comments Closed
- May 14th, 2020



CancerFax is the most trusted online platform dedicated to connecting individuals facing advanced-stage cancer with groundbreaking cell therapies.
Send your medical reports and get a free analysis.
🌟 Join us in the fight against cancer! 🌟
Привет,
CancerFax — это самая надежная онлайн-платформа, призванная предоставить людям, столкнувшимся с раком на поздних стадиях, доступ к революционным клеточным методам лечения.
Отправьте свои медицинские заключения и получите бесплатный анализ.
🌟 Присоединяйтесь к нам в борьбе с раком! 🌟