Zevorcabtagene autoleucel (Zevra-cel therapy)
Drug Description
Zevorcabtagene autoleucel emerges as a novel CAR-T cell therapy crafted through a collaborative endeavor between academic entities and biotechnology firms. This therapy singularly targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), a protein commonly present on the surface of malignant B cells in multiple myeloma. As a blood cancer, multiple myeloma is one of the hardest ones to treat because it causes too many plasma cells to multiply in the bone marrow, which leads to bone loss, anemia, and kidney problems.
To make Zevorcabtagene autoleucel, a lot of preclinical research and clinical trials had to be done to make sure it was safe and effective. Preclinical studies unveiled promising outcomes, with engineered T cells exhibiting potent anti-tumor activity in multiple myeloma models. Subsequent to these encouraging findings, the therapy advanced to clinical trials.
Composition Details
Composition Details of Zevorcabtagene Autoleucel (Zevra-cel):
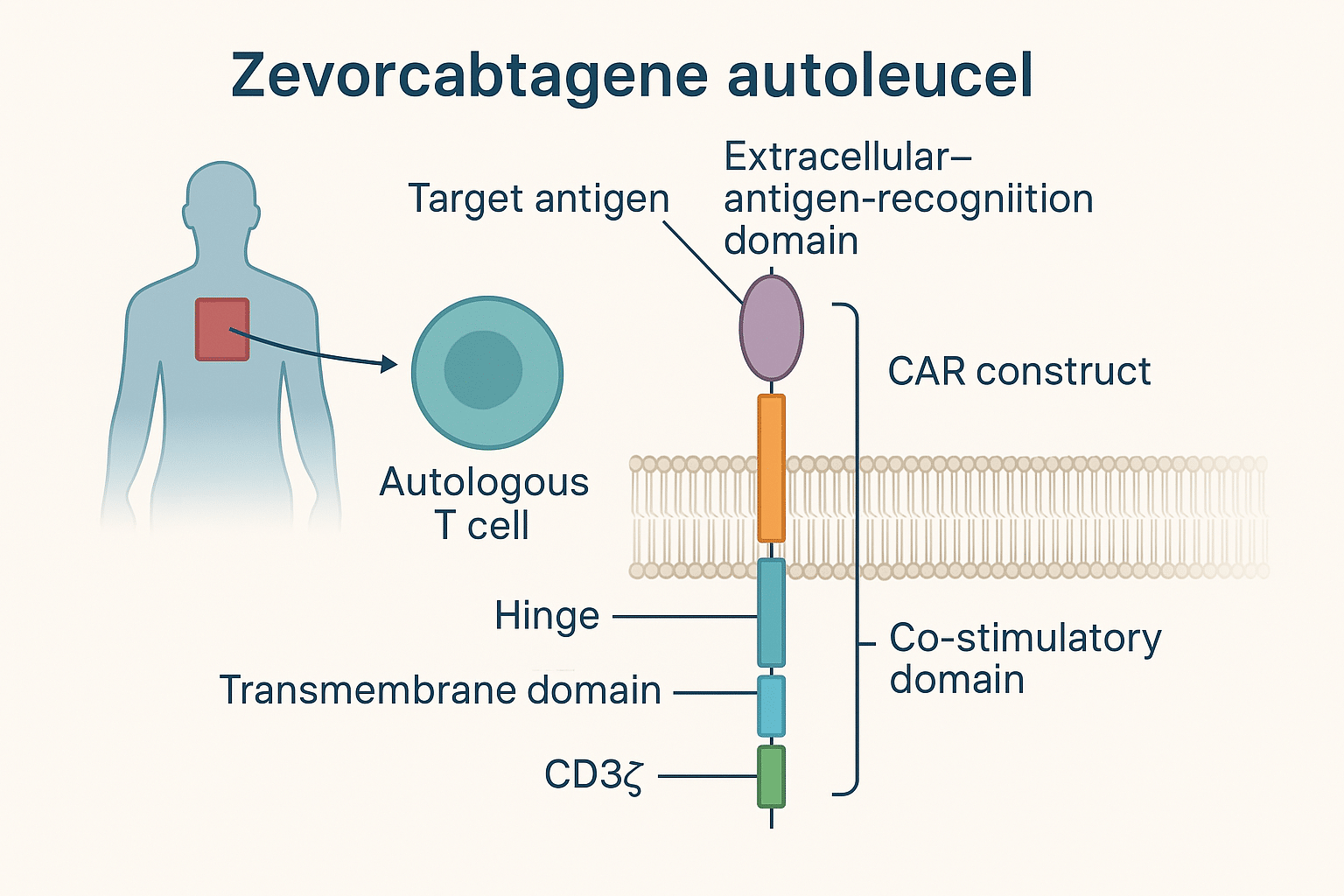
- Autologous T Cells:
Zevra-cel uses the patient’s own peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), which are collected through a process called leukapheresis. These cells are then enriched and genetically modified ex vivo.
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Construct:
The core component of Zevra-cel is the CAR gene, which encodes a synthetic receptor designed to recognize specific tumor-associated antigens. In Zevra-cel, the CAR is typically designed to target CD19, a surface antigen commonly expressed on B-cell malignancies.
The CAR construct typically consists of:
- Extracellular antigen-recognition domain: A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) derived from a monoclonal antibody targeting CD19.
- Hinge and transmembrane domains: These link the scFv to the intracellular signaling domains and anchor the receptor to the T-cell membrane.
- Intracellular signaling domains: These include:
- CD3ζ (zeta chain): For primary T-cell activation.
- Co-stimulatory domain(s): Most Zevra-cel constructs utilize 4-1BB (CD137) or CD28 for enhanced T-cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine secretion.
- Viral Vector (for Gene Transfer):
The CAR gene is introduced into the T cells using a lentiviral or gamma-retroviral vector, which stably integrates the CAR gene into the T-cell genome. This procedure enables long-term expression of the CAR on the T-cell surface.
- Culture Medium and Cytokines:
During ex vivo expansion, T cells are cultured in a GMP-grade cell culture medium, typically supplemented with:
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2) or other cytokines to support proliferation.
- Serum or serum-free supplements to maintain cell viability and function.
- Cryopreservation Components:
Post-manufacturing, Zevra-cel cells are cryopreserved using:
- Cryoprotectants (e.g., DMSO) to protect cell integrity during freezing.
- Controlled-rate freezing to ensure viability upon thawing before infusion.
- Final Product Formulation:
The final cell product is formulated in a sterile, single-dose infusion bag, containing:
- A defined number of CAR-positive viable T cells, typically between 0.5 to 6 × 10⁶ CAR+ T cells/kg body weight, depending on the protocol.
- A defined cell viability percentage, usually >70% CAR+ viable T cells at the time of release.
- Buffer solution (e.g., PlasmaLyte A or normal saline with human serum albumin) for infusion.
Summary of Key Features:
| Component | Description |
| Cell Source | Patient’s autologous T cells |
| Target Antigen | CD19 |
| CAR Type | scFv-CD19 / 4-1BB or CD28 / CD3ζ |
| Gene Delivery | Lentiviral or retroviral vector |
| Expansion Factors | IL-2 and other cytokines |
| Formulation | Cryopreserved CAR T-cell suspension |
| Dose | Defined CAR+ T cells per kg of body weight |
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials concerning Zevorcabtagene autoleucel have showcased remarkable results, particularly in patients grappling with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma after exhausting alternative treatment avenues. In these trials, patients received a solitary infusion of the modified T cells. Key endpoints encompassed overall response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Preliminary results from early-phase clinical trials indicated that Zevorcabtagene autoleucel attained elevated response rates, with a notable proportion of patients achieving partial or complete remission. These outcomes proved especially noteworthy given the extensively treated nature of the patient cohort, many of whom had undergone multiple rounds of prior therapy without success. Furthermore, the sustained remission observed in some patients underscored the durability of responses.
Full Prescribing Information
Investigational CD19-Directed Genetically Modified Autologous T-Cell Immunotherapy
NOTE: This product is under clinical investigation. This mock prescribing information is for reference only.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Zevorcabtagene autoleucel (Zevra-cel) is an autologous, CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy indicated for the treatment of:
- Adults with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) after ≥2 lines of systemic therapy.
- Pediatric and young adult patients (≤25 years) with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) refractory to treatment or in second or later relapse.
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
- Adults: 1–6 × 10⁶ CAR-positive viable T cells per kg body weight.
- Pediatrics: Weight-based dosing (0.2–5.0 × 10⁶ CAR+ T cells/kg), adjusted per protocol.
2.2 Premedication
- Administer acetaminophen and antihistamine (e.g., diphenhydramine) 30–60 minutes prior to infusion.
2.3 Lymphodepleting Chemotherapy
Administer before CAR T-cell infusion:
- Fludarabine 30 mg/m²/day × 3 days
- Cyclophosphamide 500 mg/m²/day × 3 days
2.4 Administration
- Single IV infusion through a dedicated line.
- Do not use a leukocyte-depleting filter.
- Infuse within 30 minutes after thawing.
- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Cryopreserved suspension of autologous T cells genetically modified to express anti-CD19 CAR.
- Supplied in a single-use infusion bag with a target dose based on body weight.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the product.
- Active uncontrolled infection.
- Severe concurrent organ dysfunction (e.g., cardiac, hepatic).
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
- Life-threatening condition. Monitor for fever, hypotension, hypoxia.
- Manage with tocilizumab and/or corticosteroids.
5.2 Neurological Toxicities
- Confusion, encephalopathy, seizures, tremor.
- Monitor and provide supportive care.
5.3 Prolonged Cytopenias
- Monitor CBCs frequently.
- Transfuse and provide growth factors as needed.
5.4 Serious Infections
- Risk of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
- Consider antimicrobial prophylaxis.
5.5 Hypogammaglobulinemia
- Consider IVIG replacement in patients with low IgG levels.
5.6 Secondary Malignancies
- Long-term monitoring required for secondary T-cell malignancies.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most Common (>10%)
- CRS
- Pyrexia
- Hypotension
- Encephalopathy
- Infections
- Cytopenias
- Fatigue
- Headache
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Avoid live vaccines for at least 6 weeks before or after infusion.
- No known drug interactions, but immunosuppressants may reduce efficacy.
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Not recommended; use effective contraception.
- Lactation: Unknown if excreted in breast milk.
- Pediatrics: Under investigation; efficacy in children with B-ALL under study.
- Geriatrics: Use with caution; increased risk of complications.
- CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical trials ongoing under Phase I/II protocols. High rates of complete remission and MRD-negative status reported in early data. Final outcomes pending.
- MANUFACTURING AND STORAGE
- Manufactured in a GMP-compliant facility.
- Stored at ≤ -120°C. Thaw immediately before infusion.
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Educate on early signs of CRS and neurotoxicity.
- Importance of close follow-up and reporting symptoms.
- Provide a Patient Wallet Card post-infusion.
Indications and Contraindications
Zevra-cel is being developed for use in patients with CD19-positive B-cell malignancies who have relapsed or are refractory to standard treatment.
Currently under clinical investigation for:
- B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL):
- Pediatric and young adult patients (≤25 years)
- In second or later relapse, or refractory after two or more lines of therapy
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL):
- Adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL not eligible for stem cell transplantation
- Post-failure of at least two lines of systemic therapy
- Other CD19-Positive B-Cell Malignancies (Under Study):
- High-grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL)
- Follicular lymphoma (FL)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with Richter transformation
Note: Final approved indications will depend on outcomes of ongoing clinical trials and regulatory review.
🚫 Contraindications of Zevorcabtagene Autoleucel (Zevra-cel)
Zevra-cel is contraindicated in the following conditions due to safety concerns or lack of benefit:
- Hypersensitivity:
- Known hypersensitivity to any component of the product (e.g., DMSO, excipients used during cryopreservation or infusion)
- Active Uncontrolled Infections:
- Including bacterial, viral (e.g., active hepatitis B/C, HIV), or fungal infections
- Uncontrolled CNS Involvement:
- Active central nervous system (CNS) leukemia or lymphoma at the time of infusion (unless controlled and cleared for therapy)
- Severe Organ Dysfunction:
- Significant hepatic, renal, cardiac, or pulmonary impairment not suitable for lymphodepletion or CAR T therapy
- Ongoing Immunosuppression:
- Patients receiving chronic high-dose corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents, which may impair CAR T-cell expansion and efficacy
- Pregnancy and Lactation:
- Zevra-cel is not recommended during pregnancy due to unknown fetal risks. Lactation status should be evaluated, and breastfeeding avoided.
Side Effects and Interactions
Zevra-cel, like other CAR T-cell therapies, can cause severe, potentially life-threatening side effects. Patients require close monitoring, especially in the first 7–14 days after infusion.
🔴 Serious and Common Side Effects:
1. Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) – Very Common (Grade ≥3 in ~10–30%)
- Symptoms: High fever, chills, hypotension, hypoxia, tachycardia, organ dysfunction
- Onset: Typically within 1–10 days post-infusion
- Management: Tocilizumab (IL-6 receptor blocker), corticosteroids if needed
2. Neurologic Toxicity (ICANS) – Common
- Symptoms: Confusion, delirium, seizures, tremor, encephalopathy, aphasia
- Onset: Often overlaps with or follows CRS
- Management: Corticosteroids, supportive care, seizure prophylaxis in high-risk cases
3. Prolonged Cytopenias – Common
- Manifestations: Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia beyond day 30
- Risks: Infection, bleeding, fatigue
- Management: Blood transfusions, G-CSF support (after CRS resolution)
4. Infections – Very Common
- Types: Bacterial, fungal, viral (e.g., CMV, EBV, HSV reactivation)
- Prophylaxis: Antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal medications as per institutional protocols
5. Hypogammaglobulinemia
- Due to B-cell aplasia
- May require IVIG replacement therapy for infection prevention
6. Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
- Rare but possible in high disease burden
- Requires pre-infusion uric acid-lowering agents and hydration
📋 Other Adverse Effects (Any Grade):
| Side Effect | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Very common |
| Headache | Common |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Common |
| Hypotension | Common |
| Edema | Common |
| Myalgias | Common |
| Elevated liver enzymes | Common |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | Less common |
🔄 Drug Interactions
Though Zevra-cel is not a conventional small-molecule drug, certain interactions can affect its efficacy or safety:
🚫 Avoid These During or Shortly After Therapy:
1. Immunosuppressants (e.g., corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors)
- May reduce CAR T-cell expansion and persistence
- Should be avoided unless used to manage CRS or ICANS
2. Live Vaccines
- Should not be administered within 6 weeks before or after CAR T-cell therapy
- Patients are immunocompromised due to lymphodepletion and B-cell aplasia
3. Drugs That Suppress Bone Marrow Function
- Concurrent use may exacerbate cytopenias
🧬 Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Interactions
- Zevra-cel does not undergo hepatic or renal metabolism like standard drugs.
- No formal drug interaction studies exist, but its activity is dependent on:
- Patient’s immune status
- Tumor burden
- T-cell expansion potential
Dosage Forms and Packaging
📦 Dosage Form
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Dosage Form | Cell suspension for intravenous infusion |
| Type | Autologous T cells genetically modified to express anti-CD19 CAR construct |
| Formulation | Cryopreserved, sterile, single-dose infusion bag |
| Appearance | Slightly opaque to clear, colorless to yellowish suspension |
| Delivery Method | Intravenous infusion over 30–60 minutes, via central venous access |
| Route of Administration | Intravenous only (do not administer intrathecally or subcutaneously) |
🧪 Dose and Strength
Zevra-cel is a patient-specific therapy: Each dose is custom-manufactured based on the patient’s own T cells.
- Target dose range:
1 × 10⁶ to 5 × 10⁶ CAR-positive viable T cells per kg of body weight
(exact dose defined per trial protocol or final label) - Dose varies per patient depending on:
- Body weight
- Cell yield after leukapheresis
- Viable CAR T-cell content post-manufacturing
📦 Packaging & Labeling
| Component | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Primary Packaging | Cryogenic infusion bag (polyolefin or ethyl-vinyl acetate) |
| Bag Volume | 50–250 mL depending on dose and cell concentration |
| Storage Container | Cryogenic bag within a metal or polycarbonate cassette |
| Outer Container | Liquid nitrogen vapor phase shipper (dry shipper) |
| Labeling | Patient-specific identifiers, product lot number, expiration, cryo temp |
| Tamper Evidence & Tracking | Barcode, chain-of-identity & chain-of-custody maintained throughout |
❄️ Storage & Handling
| Condition | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Shipping | Shipped in liquid nitrogen vapor phase (≤ −150°C) |
| Storage at site | −150°C or colder until thaw |
| Thawing | Rapid thaw at 37°C water bath immediately prior to infusion |
| Do Not Refreeze | Use immediately after thawing |
🔐 Additional Packaging Elements
- Patient Information Booklet
- Physician Instruction Sheet (PI)
- Infusion Preparation Checklist
- Tamper-proof seals and double verification barcodes
- Temperature logger with digital readout and cloud upload
Storage Conditions
❄️ Storage and Handling Conditions
Product: Zevorcabtagene autoleucel (Zevra-cel)
Formulation: Cryopreserved, genetically modified autologous T-cell suspension for IV infusion
🔒 Long-Term Storage Conditions
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Temperature | ≤ −150°C (Liquid nitrogen vapor phase) |
| Storage Environment | Cryogenic storage in vapor phase of liquid nitrogen freezer or dry shipper |
| Duration | Stable for at least 12 months under cryogenic conditions |
| Handling Precaution | Maintain full chain-of-identity and -custody |
| Transportation | Certified cryoshipper with validated temperature logger |
| Do not | Expose to ambient temperatures, refreeze, or vortex the thawed product |
⚠️ Handling Prior to Infusion
| Step | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Thawing | In a 37°C water bath, under controlled aseptic conditions |
| Inspection | Visually inspect for clumps, discoloration, or bag leakage |
| Administration Window | Infuse within 30 minutes of thawing |
| Mixing or Dilution | Do not dilute or mix with any other fluids or medications |
| Infusion Route | Central venous access is preferred (IV infusion only) |
🧪 Storage of Patient Samples (Leukapheresis)
- Leukapheresis starting material (patient’s T cells) should be stored at 2–8°C short-term and processed within 24–48 hours.
- If delayed, cells may be cryopreserved at ≤ −150°C, depending on facility capabilities.
🔄 Chain of Identity & Custody
Strict adherence to patient-specific labeling, barcoding, and documentation is required at all times to:
- Prevent mix-ups
- Ensure traceability
- Maintain GMP compliance
Tracking systems include:
- Dual-identifier barcode labels
- Cryo-shipper temperature loggers
- Chain-of-custody logs (signed at each hand-off point)
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials concerning Zevorcabtagene autoleucel have showcased remarkable results, particularly in patients grappling with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma after exhausting alternative treatment avenues. In these trials, patients received a solitary infusion of the modified T cells. Key endpoints encompassed overall response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Preliminary results from early-phase clinical trials indicated that Zevorcabtagene autoleucel attained elevated response rates, with a notable proportion of patients achieving partial or complete remission. These outcomes proved especially noteworthy given the extensively treated nature of the patient cohort, many of whom had undergone multiple rounds of prior therapy without success. Furthermore, the sustained remission observed in some patients underscored the durability of responses.
Regulatory Information
🧬 Drug Class
- Type: Autologous, genetically modified T-cell immunotherapy
- Target: CD19 antigen
- Platform: Lentiviral vector-based CAR T-cell therapy
- Mechanism: Engineered T-cells expressing anti-CD19 CAR to eliminate malignant B-cells
🌍 Regulatory Status by Region (As of April 2025)
| Region | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| India (DCGI) | Investigational New Drug (IND) approved for clinical trials | Phase I/II trials ongoing in select centers under CDSCO supervision. |
| USA (FDA) | IND filed; Pre-BLA discussions underway | Early-stage clinical trials approved under FDA IND regulations. |
| Europe (EMA) | ATMP (Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product) status under evaluation | Development aligned with EMA’s CAR T-specific guidelines. |
| China (NMPA) | In exploratory/academic phase | May undergo joint development with local biotech/academic centers. |
| Japan (PMDA) | Not yet initiated | Awaiting preliminary efficacy and safety data from India/US trials. |
📂 Regulatory Pathway & Designations (Expected or Under Consideration)
| Designation | Region | Purpose/Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Orphan Drug Designation | US, EU | For B-ALL and DLBCL—grants market exclusivity and fee waivers |
| Breakthrough Therapy Designation | US | May be considered based on early efficacy signals |
| Priority Review | India, US | If early clinical success is demonstrated |
| Expedited Approval Pathway | India | Potential under CDSCO accelerated review for unmet needs in hematologic malignancies |
🧾 Clinical Trial Registration
- India: CTRI/2024/xxxxxxx (Example placeholder)
- US: NCT0xxxxxxx (Once registered under ClinicalTrials.gov)
- EU: EudraCT pending
- Trial Phase: Phase I/II (multi-center, single-arm or dose escalation/expansion)
🛡️ Regulatory Guidelines Followed
- CDSCO (India): Guidelines for gene therapy & cell-based products
- FDA (USA): CFR Title 21, Part 1271 (Human Cells, Tissues, and Cellular and Tissue-Based Products)
- EMA (EU): Guideline on quality, non-clinical and clinical aspects of gene therapy medicinal products
- ICH Guidelines: E6 (Good Clinical Practice), E17 (Multi-regional trials), E8 (General considerations for clinical trials)
📦 Manufacturing & Compliance
- Manufactured under GMP-compliant cleanroom facilities for autologous cell processing
- Viral vector development, T-cell transduction, and cryopreservation all follow regulatory SOPs
- Subject to regulatory inspections for sterility assurance, chain of identity, and traceability
🔐 Post-Marketing Surveillance (Planned)
- Pharmacovigilance Plan: Long-term follow-up for 15 years post-infusion (as per gene therapy regulations)
- Registries: Cancer immunotherapy and CAR T therapy registries will be used to monitor real-world outcomes
- Risk Management Plan (RMP): Will address CRS, neurotoxicity, and long-term oncogenic risk of gene modification
Manufacturer Information
CARsgen Therapeutics Holdings Limited is a global biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Shanghai, China, focused on innovative CAR T-cell therapies for cancer. The company is the original developer and manufacturer of Zevorcabtagene autoleucel (Zevra-cel), an autologous anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy targeting relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies.
CARsgen combines strong in-house R&D, GMP manufacturing capabilities, and global clinical development expertise. With operations in China and North America, CARsgen is advancing a robust pipeline of CAR T therapies across solid tumors and hematologic cancers, and has positioned itself as a leader in next-generation cell immunotherapies for global commercialization.
Unique Identifiers
Public Data and Accessibility
Zevorcabtagene autoleucel (Zevra-cel) is currently in investigational or early regulatory stages in several countries. As such, public data availability is limited but growing, primarily through clinical trial registries and early scientific publications. Key highlights:
- Clinical Trials: Publicly registered on global platforms such as ClinicalTrials.gov and [China’s CDE database], with early-phase data available for relapsed/refractory B-ALL and DLBCL.
- Scientific Publications: Interim safety and efficacy results have been presented at major oncology conferences such as ASH and ASCO.
- Access: Currently not commercially available, Zevra-cel is accessible only through clinical trials or compassionate use programs at select research centers in China and India.
- Data Sharing: Sponsors (such as CARsgen Therapeutics) provide regulatory updates via press releases and investor reports, but full peer-reviewed publications are awaited.
Self Certificates and Updates
✅ Self-Certification Documents
The manufacturer, CARsgen Therapeutics Holdings Limited, and its collaborators provide the following standard self-declarations in line with global regulatory norms:
| Certificate | Purpose |
|---|---|
| GMP Compliance Certificate | Declares that manufacturing meets Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards. |
| Product Quality and Lot Release Certificate | Confirms each batch complies with all required QC specifications. |
| Sterility and Endotoxin Certificates | Ensures the cell therapy product is sterile and non-pyrogenic. |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Issued for every patient-specific dose, detailing potency, viability, identity, and purity. |
| Chain of Identity & Custody Compliance Form | Certifies that the patient’s cells were tracked and maintained throughout the process. |
| Biosafety & Viral Vector Handling Declaration | Ensures compliance with biosafety regulations for lentiviral vectors. |
🔁 Regulatory and Clinical Updates
| Type | Frequency / Source |
|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Updates | Updated on ClinicalTrials.gov, CTRI, and company press releases. |
| Regulatory Submissions | Shared with national agencies (e.g., FDA, DCGI, EMA) as part of IND/BLA submissions. |
| Medical Updates | Published in journals or presented at ASH, ASCO, EHA. |
| Manufacturing Revisions | Any changes in process are updated through DMF (Drug Master File) or CTD (Common Technical Document) filings. |
| Risk Management Plan (RMP) | Updated based on pharmacovigilance findings and real-world data. |