Immuno-oncology is a way to treat cancer by using the body’s immune system. BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) technology is a targeted immuno-oncology platform that binds a patient’s own T cells to cancer cells. Because BiTE technology is flexible, it is easy to make molecules that attack tumor-specific antigens, which makes immuno-oncotherapy possible. Blinatumomab was the first standard BiTE molecule to be approved. It targets CD19 surface antigens on B cells and is mostly unaffected by genetic changes or escape mechanisms inside cells. More BiTE molecules are being made to treat other blood cancers (like multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukaemia, and B-cell Xodgkin bo'lmagan limfoma) and solid tumours (like prostate cancer, glioblastoma, stomach cancer, and small-cell lung cancer). BiTE molecules that have a longer half-life than the standard ones are also being made. With BiTE technology, advances in immuno-oncology could make it easier to treat both blood and solid tumours and make them more effective when used with other treatments.
BiTe terapiyasi nima?
Immuno-oncology therapies are scientifically proven ways to treat different types of solid and qon saratoni. Hematologic cancers are a good fit for treatments that target the immune system because cancerous blood cells move around with immune cells. Several immunoterapiya saraton kasalligini davolash ishlari olib borilmoqda.
Monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitors that stop the binding of checkpoint proteins (like PD-1 and CTLA-4) are useful against many types of cancer. They work well and are safe for many solid tumours, especially when they target PD-1. Non-small-cell lung, kidney, and bladder cancers have all been treated successfully with these drugs. But many people don’t react to checkpoint inhibitors or get sick again after taking them. Except for non-Hodgkin limfoma, most results on hematologic cancers have been disappointing, especially for myeloma and leukaemia, where the overall response rate in approved indications ranges from 12.0% to 48.5%.8-15.
Other immuno-oncology treatments, on the other hand, have a higher success rate. Chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies change a patient’s T cells to attack a specific cellular antigen, such as CD19 in the treatment of B-cell malignancies and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in the treatment of ko'p mieloma (MM). CAR T-cell treatments have shown promise in treating hematologic cancers. They haven’t been as effective in treating solid tumours, but there have been some good results with neyroblastoma, human epidermal growth factor receptor tumours, and non-small-cell lung cancer. The genetic modification and in vitro multiplication of T cells take a long and complicated manufacturing process. This is a downside of this therapy because it makes it harder for patients to get this treatment quickly and in large numbers. The fact that lymphodepletion through chemotherapy preparation must be done first as a requirement for improved effectiveness is also a drawback.
BiTE (bispesifik T-hujayra ishtirokchisi) terapiyasi bemorning T hujayralarini o'simtada ifodalangan antijenler bilan bog'laydi. Bu T hujayralari genlarini o'zgartirmasdan yoki ularni tanadan tashqarida o'stirish yoki manipulyatsiya qilmasdan saratonni o'ldirish uchun bemorning o'z T hujayralarining sitotoksik qobiliyatini yoqadi. BiTE molekulalari ularni yanada samaraliroq qilish uchun dori sifatida yoki boshqa davolash usullari bilan birga ishlatilishi mumkin.
BiTe ta'sir qilish mexanizmi
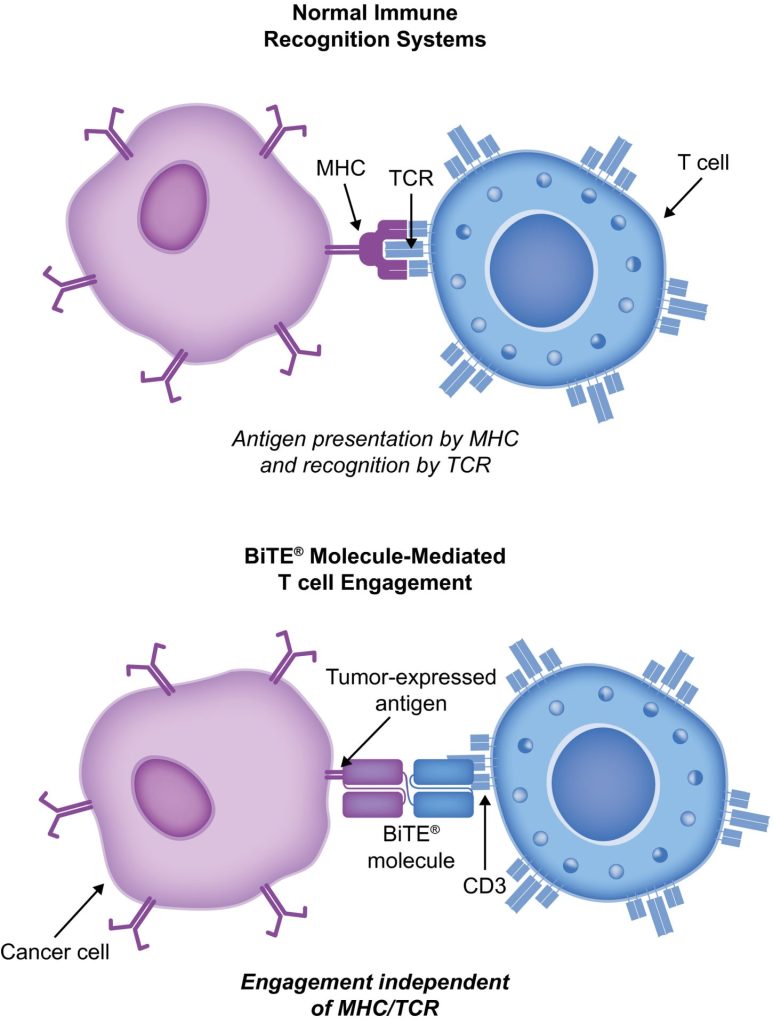
BiTE molecules are antibody constructs with two binding domains. One recognises tumor-expressed antigens (such as BCMA, CD19, or -like protein [DLL3]), and the other, CD3, recognises T cells (Fig. 1). Two single-chain variable fragment (scFv) regions from monoclonal antibodies are connected by a flexible peptide linker to make the binding domains. The first scFv binding region can be changed to target any surface antigen, so it can be used right away to treat a wide range of tumours and can be used again later. The second scFv binding region always binds to CD3, which is a part of the T-cell receptor complex that never changes. When a BiTE molecule interacts with both a cytotoxic T cell and a tumour cell, the T cells begin to multiply. This increases the amount of effector cells and makes BiTE therapy more effective. Then, the death of cancer cells is started. BiTE molecules can get any T cells to do this because they don’t need co-stimulation or the usual processes of the major histocompatibility complex.
Blinatumomab is the first and only BiTE therapy that has been approved. It targets the CD19 receptor on both normal and cancerous B cells. It is a highly potent molecule with cytotoxic effects seen at low exposures (10–100 pg/mL)26. In its presence, T cells can perform serial-target lysis, quickly binding to and killing many cells. This is how BiTE therapies work, and it can be seen in other BiTE molecules that are still in research. In o'tkir limfoblastik leykemiya (ALL), blinatumomab has been shown to be effective and safe. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration gave it fast approval, and in 2017, it got full approval for relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL. In 2018, accelerated approval was given to blinatumomab for treating BCP-ALL with minimum residual disease (MRD). This was the first approval for this use. In November 2015, the European Medicines Agency also gave it a green light for BCP-ALL with a Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) that is negative and R/R. Blinatumomab is approved for R/R BCP-ALL in adults and children in 57 countries, including Japan, all countries in the European Union, Canada, and Australia.
Blinatumomab BCP-ALL bilan kasallangan bemorlarni davolash uchun
Blinatumomab BCP-ALL davolash usulini o'zgartirdi. Standart parvarishlash (SOC) kimyoterapiyasi bilan solishtirganda, u umumiy omon qolishni (OS) oshirdi va ma'lum yon ta'sirlar (AE) sonini kamaytirdi. Bir qator muhim tadqiqotlar, jumladan, randomizatsiyalangan nazorat ostidagi tadqiqotlar shuni ko'rsatdiki, blinatumomab xavfsiz va BCP-ALL uchun ham kattalar, ham bolalar uchun ishlaydi. CAR T-hujayra terapiyasi, R/R BCP-ALL va T-hujayra ALL bo'lgan 2 ta bola (01626495–01029366 yosh) va 25 nafar kattalar (5–22 yosh) davolangan 5 ta bitta qo'l tadqiqoti (clinicaltrials.gov IDs NCT26 va NCT60) ma'lumotlari mavjud. Ammo natijalar umid baxsh etadi (90% da toʻliq javob [CR], 6 oylik hodisalarsiz omon qolish bilan barqaror remissiya 67% va umumiy omon qolish [OS] darajasi 78% [oʻrtacha kuzatuv, 7 oy; diapazon, 1–24 oy]).
TOWER tadqiqoti (3-bosqich, tasodifiy, ochiq yorliqli tadqiqot, ALL relapsli/refrakter B-prekursorli kattalardagi bemorlarda BiTE antikori Blinatumomabning parvarishlash standartiga nisbatan samaradorligini o‘rganish; clinicaltrials.gov identifikatori NCT02013167b mononomali mononomasi bilan solishtirganda) y Ph-salbiy, R/R BCP-ALL bilan og'ir oldindan davolangan kattalarda. Odamlar uzoq umr ko'rganligi sababli, tadqiqot erta to'xtatildi. Blinatumomab guruhidagi AE lar avvalgi tadqiqotlarda kuzatilganlar bilan bir xil edi va blinatumomab SOCga qaraganda pastroq ta'sir qilish bilan sozlangan AE stavkalariga ega edi.34 Blinatumomab shuningdek, Ph-musbat, R/R BCP-ALL va Ph-salbiy, R/R BCP-ALL bo'lgan bolalar uchun ishlaydi.
30% to 50% of people with BCP-ALL in complete hematologic remission show persistent MRD. In the single-arm, phase 2 BLAST study (A Confirmatory Multicenter, Single-Arm Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of the BiTE Antibody Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With MRD of B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia; clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01207388), blinatumomab was tested on patients with BCP-ALL in first or later complete After blinatumomab treatment, 78% of patients who were MRD positive became MRD negative. The 5-year OS study showed a median OS of 36.5 months, and more than half of those who had a complete MRD response after the first cycle of blinatumomab were still alive at 5 years, which suggests that the treatment might be able to cure some patients. AEs were seen that were linked to sitokinlarni chiqarish sindromi (CRS).31 Other studies, like NCT03023878 and NCT03340766, are still looking at blinatumomab in first-line settings and in combination with other treatments.
CD19-targeted treatments have been linked to failure because of the loss of CD19 antigen after treatment. The failure rates for blinatumomab range from 8% to 35%, and for CAR T-hujayrali terapiya, they range from 39% to 65%.36-40 We don’t fully understand what causes therapy to fail, but one possibility is immunoediting, in which antigen loss is caused by a T-cell-dependent process called immunoselection, which lets tumour cells get away.41 Lineage switch and epitope loss under therapy pressure have also been suggested as ways for tumours to escape treatment. However, a recent study on epitope loss found that some CD19 isoforms that help CAR T-cells escape were already present at the time of diagnosis. This suggests that combining treatments might be helpful. Another thing that can cause immunotherapy to fail is called “inhibitory T-cell signalling.” In this case, the blocking programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is interesting because it is more common in B-cell ALL cells from patients who don’t respond to blinatumomab and can make CD3 BiTE molecules less effective.43 By making a CD28/PD-L1 BiTE that triggers the CD28 co-stimulatory signal instead of the inhibitory signaling pathway that is usually seen when a T cell binds to a PD-L1-expressing cancer cell, this inhibition could be turned off.43 Dual-targeted CAR T cells are also being looked into as a way to make up for the loss of tumour antigens. This can be done by modifying each T cell with 2 CAR molecules and 2 different binding domains (dual-signaling CAR) or by putting 2 different binding domains on 1 CAR molecule at the same time (TanCAR).
BiTE va uni boshqarish bilan bog'liq noxush hodisalar
Blinatumomabning klinik tadkikotlarida eng keng tarqalgan AE isitma, past oq qon hujayralari soni va past trombotsitlar soni. Eng muhim xavflardan ba'zilari CRS, neyrotoksiklik va dori xatolaridir. Neyrotoksiklik CD19-ga xos CAR T-hujayralarini davolashda ham sodir bo'lishi mumkin, ammo bu CD19 tufayli bo'lmasligi mumkin. CD1/CD1 maqsadlari haqida hali ham davom etayotgan 20/3b fazasi tadqiqotining natijalari shuni ko'rsatdiki, 3 yoki undan yuqori darajadagi CNS AE kamdan-kam uchraydi (barcha 3 darajali AE ning 3%). Ko'pincha blinatumomabning CRSga reaktsiyasi engil, ammo kamdan-kam hollarda u og'ir va hatto hayot uchun xavfli bo'lishi mumkin. Yallig'lanish reaktsiyalarini kortikosteroidlar bilan kamaytirish mumkin. CRS ehtimolini kamaytirish uchun, blinatumomabning birinchi dozasidan oldin prednizon yoki deksametazon infuzionini berish va dozani asta-sekin oshirish yaxshidir. Boshqa BiTE molekulalaridan oldin kortikosteroidlarni qo'llash, boshqa BiTE molekulalarini qo'llashda deksametazonni premedikatsiya sifatida ishlatishga sabab bo'ldi. Biroq, bu ta'sirni butun BiTE platformasiga qo'llash mumkinmi yoki yo'qmi, aniq emas va CRS bilan kurashishning boshqa usullari ko'rib chiqilmoqda. Interleykin 6 - bu CRS ni keltirib chiqaradigan sitokin va u bilan kasallangan odamlarda yuqori. Interleykin-6 retseptorlarini bloklaydigan tosilizumab CAR T-hujayralarini davolashdan so'ng juda yomon bo'lgan CRSni davolash uchun ishlatilgan.49 Kasalxonada CRSni davolash uchun o'simta nekrozi omil-ingibitorlari ham qo'llanilgan.