Immuno-oncology is a way to treat cancer by using the body’s immune system. BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) technology is a targeted immuno-oncology platform that binds a patient’s own T cells to cancer cells. Because BiTE technology is flexible, it is easy to make molecules that attack tumor-specific antigens, which makes immuno-oncotherapy possible. Blinatumomab was the first standard BiTE molecule to be approved. It targets CD19 surface antigens on B cells and is mostly unaffected by genetic changes or escape mechanisms inside cells. More BiTE molecules are being made to treat other blood cancers (like multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukaemia, and B-cell qanjirada unugyada 'Hodgkin') and solid tumours (like prostate cancer, glioblastoma, stomach cancer, and small-cell lung cancer). BiTE molecules that have a longer half-life than the standard ones are also being made. With BiTE technology, advances in immuno-oncology could make it easier to treat both blood and solid tumours and make them more effective when used with other treatments.
Waa maxay daawaynta BiTe?
Immuno-oncology therapies are scientifically proven ways to treat different types of solid and kansarka dhiigga. Hematologic cancers are a good fit for treatments that target the immune system because cancerous blood cells move around with immune cells. Several immunotherapy daawaynta kansarka ayaa ku jirta shaqada.
Monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitors that stop the binding of checkpoint proteins (like PD-1 and CTLA-4) are useful against many types of cancer. They work well and are safe for many solid tumours, especially when they target PD-1. Non-small-cell lung, kidney, and bladder cancers have all been treated successfully with these drugs. But many people don’t react to checkpoint inhibitors or get sick again after taking them. Except for non-Hodgkin qanjiro, most results on hematologic cancers have been disappointing, especially for myeloma and leukaemia, where the overall response rate in approved indications ranges from 12.0% to 48.5%.8-15.
Other immuno-oncology treatments, on the other hand, have a higher success rate. Chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies change a patient’s T cells to attack a specific cellular antigen, such as CD19 in the treatment of B-cell malignancies and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in the treatment of Meelo badan (MM). CAR T-cell treatments have shown promise in treating hematologic cancers. They haven’t been as effective in treating solid tumours, but there have been some good results with neuroblastoma, human epidermal growth factor receptor tumours, and non-small-cell lung cancer. The genetic modification and in vitro multiplication of T cells take a long and complicated manufacturing process. This is a downside of this therapy because it makes it harder for patients to get this treatment quickly and in large numbers. The fact that lymphodepletion through chemotherapy preparation must be done first as a requirement for improved effectiveness is also a drawback.
Daawaynta BiTE (bisspecific T-cell engager) waxay ku xidhaa unugyada T ee bukaanka iyo antigens-ka buro-muujinta. Tani waxay daartaa awoodda cytotoxic ee unugyada T ee bukaanku si ay u dilaan kansarka iyaga oo aan beddelin hiddo-wadaha unugyada T ama u baahan in ay koraan ama ku dhaqmaan meel ka baxsan jidhka. Unugyada 'BiTE molecules' waxa keligood loo isticmaali karaa daawo ahaan ama daawaynta kale si looga dhigo kuwo waxtar leh.
Habka waxqabadka
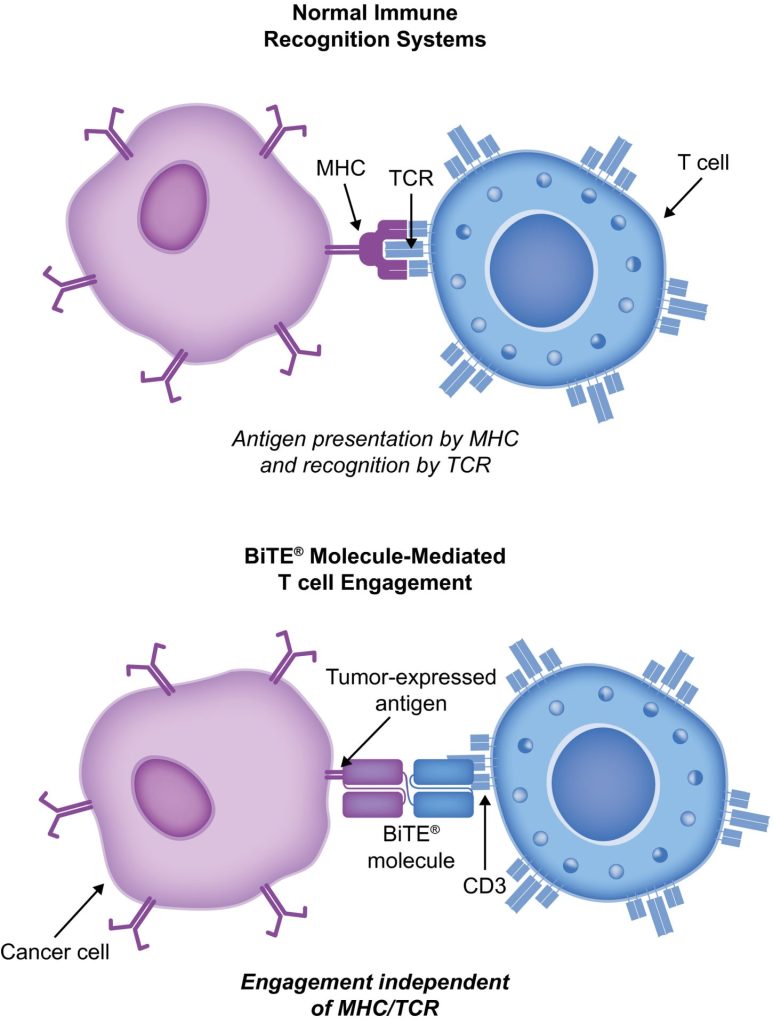
BiTE molecules are antibody constructs with two binding domains. One recognises tumor-expressed antigens (such as BCMA, CD19, or -like protein [DLL3]), and the other, CD3, recognises T cells (Fig. 1). Two single-chain variable fragment (scFv) regions from monoclonal antibodies are connected by a flexible peptide linker to make the binding domains. The first scFv binding region can be changed to target any surface antigen, so it can be used right away to treat a wide range of tumours and can be used again later. The second scFv binding region always binds to CD3, which is a part of the T-cell receptor complex that never changes. When a BiTE molecule interacts with both a cytotoxic T cell and a tumour cell, the T cells begin to multiply. This increases the amount of effector cells and makes BiTE therapy more effective. Then, the death of cancer cells is started. BiTE molecules can get any T cells to do this because they don’t need co-stimulation or the usual processes of the major histocompatibility complex.
Blinatumomab is the first and only BiTE therapy that has been approved. It targets the CD19 receptor on both normal and cancerous B cells. It is a highly potent molecule with cytotoxic effects seen at low exposures (10–100 pg/mL)26. In its presence, T cells can perform serial-target lysis, quickly binding to and killing many cells. This is how BiTE therapies work, and it can be seen in other BiTE molecules that are still in research. In lymphoblastic leukemia ba'an (ALL), blinatumomab has been shown to be effective and safe. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration gave it fast approval, and in 2017, it got full approval for relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL. In 2018, accelerated approval was given to blinatummab for treating BCP-ALL with minimum residual disease (MRD). This was the first approval for this use. In November 2015, the European Medicines Agency also gave it a green light for BCP-ALL with a Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) that is negative and R/R. Blinatumomab is approved for R/R BCP-ALL in adults and children in 57 countries, including Japan, all countries in the European Union, Canada, and Australia.
Blinatumomab ee daawaynta bukaanada qaba BCP-ALL
Blinatumomab waxay beddeshay habka loo daweeyo BCP-ALL. Marka la barbar dhigo kiimoterabiga caadiga ah ee daryeelka (SOC), waxay kordhisay badbaadada guud (OS) waxayna hoos u dhigtay tirada waxyeellooyinka qaarkood (AEs). Daraasado dhowr ah oo muhiim ah, oo ay ku jiraan tijaabooyinka la kantaroolay ee aan kala sooc lahayn, ayaa muujiyay in blinatumomab ay badbaado tahay oo ay u shaqeyso BCP-ALL ee dadka waaweyn iyo carruurta labadaba. CAR T-cell daaweynta, waxaa jira xog kaliya oo laga helay 2 daraasadood oo cudud ah (clinicaltrials.gov IDs NCT01626495 iyo NCT01029366) kuwaas oo 25 caruur ah (da'da 5-22) iyo 5 qaangaar ah (da'da 26-60) oo leh R/R BCP-ALL iyo T-cell ALL lagu daaweeyay. Laakiin natiijadu waa rajo (jawaab dhamaystiran [CR] ee 90%, cafis joogta ah oo leh 6-bilood oo badbaado bilaash ah oo ku jira 67%, iyo guud ahaan badbaadada [OS] ee 78% [la-socod dhexdhexaad ah, bilaha 7; kala duwan, 1-24 bilood]).
Daraasadda TOWER (Wajiga 3, Randomized, Daraasad Summada Furan ee Baadhista Waxtarka BiTE Antibody Blinatumomab Versus Standard of Care Chemotherapy ee Mawduucyada Dadka Waaweyn ee Soo Noqnoqday/Dib-u-noqoshada B-Precursor ALL; Clinicaltrials.gov identifier pre-chemomatherapy NCT02013167) dadka waaweyn ee qaba Ph-negative, R/R BCP-ALL. Sababtoo ah dadku waxay noolaayeen waqti dheer, daraasadda ayaa la joojiyay goor hore. AE-yada kooxda blinatumomab waxay la mid yihiin kuwii lagu arkay daraasadihii hore, iyo blinatumomab waxay lahaayeen hoos u dhigista soo-gaadhista-soo-gaadhista heerka AE marka loo eego SOC.34 Blinatumomab sidoo kale waxay u shaqeysaa dadka qaba Ph-positive, R/R BCP-ALL iyo carruurta leh Ph-negative, R/R BCP-ALL.
30% to 50% of people with BCP-ALL in complete hematologic remission show persistent MRD. In the single-arm, phase 2 BLAST study (A Confirmatory Multicenter, Single-Arm Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of the BiTE Antibody Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With MRD of B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia; clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01207388), blinatumomab was tested on patients with BCP-ALL in first or later complete After blinatumomab treatment, 78% of patients who were MRD positive became MRD negative. The 5-year OS study showed a median OS of 36.5 months, and more than half of those who had a complete MRD response after the first cycle of blinatumomab were still alive at 5 years, which suggests that the treatment might be able to cure some patients. AEs were seen that were linked to cytokine sii daayo syndrome (CRS).31 Other studies, like NCT03023878 and NCT03340766, are still looking at blinatumomab in first-line settings and in combination with other treatments.
CD19-targeted treatments have been linked to failure because of the loss of CD19 antigen after treatment. The failure rates for blinatumomab range from 8% to 35%, and for CAR T-cell daawaynta, they range from 39% to 65%.36-40 We don’t fully understand what causes therapy to fail, but one possibility is immunoediting, in which antigen loss is caused by a T-cell-dependent process called immunoselection, which lets tumour cells get away.41 Lineage switch and epitope loss under therapy pressure have also been suggested as ways for tumours to escape treatment. However, a recent study on epitope loss found that some CD19 isoforms that help CAR T-cells escape were already present at the time of diagnosis. This suggests that combining treatments might be helpful. Another thing that can cause immunotherapy to fail is called “inhibitory T-cell signalling.” In this case, the blocking programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is interesting because it is more common in B-cell ALL cells from patients who don’t respond to blinatumomab and can make CD3 BiTE molecules less effective.43 By making a CD28/PD-L1 BiTE that triggers the CD28 co-stimulatory signal instead of the inhibitory signaling pathway that is usually seen when a T cell binds to a PD-L1-expressing cancer cell, this inhibition could be turned off.43 Dual-targeted CAR T cells are also being looked into as a way to make up for the loss of tumour antigens. This can be done by modifying each T cell with 2 CAR molecules and 2 different binding domains (dual-signaling CAR) or by putting 2 different binding domains on 1 CAR molecule at the same time (TanCAR).
Dhacdooyinka xun xun ee BiTE iyo maamulkeeda
Daraasadaha kiliinikada ee blinatummab, AE-yada ugu caansan waa qandho, tirada unugyada dhiigga cad oo hooseeya, iyo tirada platelet oo hooseeya. Qaar ka mid ah khataraha ugu muhiimsan waa CRS, neurotoxicity, iyo khaladaadka daroogada. Neurotoxicity waxay sidoo kale ku dhici kartaa daawaynta CD19-gaar ah ee CAR T-cell, laakiin waxaa laga yaabaa inaysan sabab u ahayn CD19. Natiijooyinka daraasadda wejiga 1/1b ee weli socda oo ku saabsan bartilmaameedyada CD20/CD3 waxay muujisay in CNS AE ee fasalka 3 ama ka sarreeya ay naadir ahaayeen (3% dhammaan fasallada 3 AEs). Inta badan, falcelinta blinatumomab ee CRS waa mid fudud, laakiin xaalado dhif ah, waxay noqon kartaa mid daran oo xitaa nafta halis gelisa. Dareen-celinta bararka ayaa lagu yarayn karaa corticosteroids. Si loo yareeyo fursadda CRS, waxa fiican in la siiyo faleebo prednisone ama dexamethasone ka hor qiyaasta koowaad ee blinatummab iyo in la kordhiyo qiyaasta si tartiib ah. Isticmaalka corticosteroids ka hor molecules kale ee BiTE waxay siisay sabab loo isticmaalo dexamethasone daawo ahaan marka la isticmaalayo molecules kale ee BiTE. Si kastaba ha ahaatee, ma cadda in saameyntan lagu dabaqi karo dhammaan goobta BiTE, iyo siyaabo kale oo wax looga qabto CRS ayaa la eegayaa. Interleukin 6 waa cytokine sababa CRS waxaana ku badan dadka qaba. Tocilizumab, oo xannibaya soo-dhoweynta interleukin-6, ayaa loo isticmaalay in lagu daweeyo CRS oo aad u xun ka dib daaweynta CAR T-cell.